Deoxyandrographolide
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 11:26:09
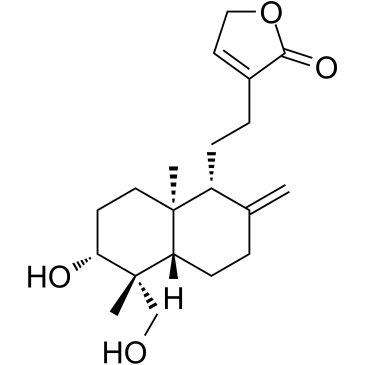
Deoxyandrographolide structure
|
Common Name | Deoxyandrographolide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79233-15-1 | Molecular Weight | 334.450 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 511.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 178.2±23.6 °C | |
Use of DeoxyandrographolideDeoxyandrographolide is a natural compound extracted from A. paniculata; potently inhibit the growth of liver (HepG2 and SK-Hep1) and bile duct (HuCCA-1 and RMCCA-1) cancer cells.IC50 value:Target: Anticancer natural compoundin vitro: Treatment with 14-DAG activated AMPK through induction of cyclic AMP-protein kinase A pathway. 14-DAG controlled ethanol-induced hepatosteatosis by interfering with dysregulation of lipid metabolism. In conclusion, our results indicated that 14-DAG was capable of preventing the development of fatty liver through AMPK-mediated regulation of lipid metabolism [1]. 14-DAG down-regulated the formation of death-inducing signalling complex, resulting in desensitization of hepatocytes to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Pretreatment of hepatocytes with 14-DAG accentuated microsomal Ca-ATPase activity through induction of NO/cGMP pathway [2]. 14-DAP, in concentrations between 10-100 microM, reduced the extracellular acidification rate and the intracellular alkalinization in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, 14-DAP reduced PAF-induced calcium flux in the presence of extracellular calcium, and tyrosine phosphorylation of a 44 kDa protein corresponding to the MAPK(ERK1) [3]. in vivo: Half of the ethanol-fed animals received 14-deoxyandrographolide (14-DAG) treatment for the last 4 weeks of study. protective effect of 14-DAG against ethanol-induced hepatic injury is based on its ability to reduce oxidative stress through cNOS dependent improvement of redox status. 14-DAG mediated activation of adenylate cyclase-cAMP signaling leading to up-regulation of cNOS may provide a promising approach in the prevention of liver diseases during chronic alcoholism [4]. |
| Name | 4-[2-[(4aS,5R,6R,8aR)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5,8a-trimethyl-3,4,4a,6,7,8-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl]ethyl]-2H-furan-5-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Deoxyandrographolide is a natural compound extracted from A. paniculata; potently inhibit the growth of liver (HepG2 and SK-Hep1) and bile duct (HuCCA-1 and RMCCA-1) cancer cells.IC50 value:Target: Anticancer natural compoundin vitro: Treatment with 14-DAG activated AMPK through induction of cyclic AMP-protein kinase A pathway. 14-DAG controlled ethanol-induced hepatosteatosis by interfering with dysregulation of lipid metabolism. In conclusion, our results indicated that 14-DAG was capable of preventing the development of fatty liver through AMPK-mediated regulation of lipid metabolism [1]. 14-DAG down-regulated the formation of death-inducing signalling complex, resulting in desensitization of hepatocytes to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Pretreatment of hepatocytes with 14-DAG accentuated microsomal Ca-ATPase activity through induction of NO/cGMP pathway [2]. 14-DAP, in concentrations between 10-100 microM, reduced the extracellular acidification rate and the intracellular alkalinization in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, 14-DAP reduced PAF-induced calcium flux in the presence of extracellular calcium, and tyrosine phosphorylation of a 44 kDa protein corresponding to the MAPK(ERK1) [3]. in vivo: Half of the ethanol-fed animals received 14-deoxyandrographolide (14-DAG) treatment for the last 4 weeks of study. protective effect of 14-DAG against ethanol-induced hepatic injury is based on its ability to reduce oxidative stress through cNOS dependent improvement of redox status. 14-DAG mediated activation of adenylate cyclase-cAMP signaling leading to up-regulation of cNOS may provide a promising approach in the prevention of liver diseases during chronic alcoholism [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 511.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 334.450 |
| Flash Point | 178.2±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 334.214417 |
| PSA | 66.76000 |
| LogP | 2.55 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.535 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~% 
Deoxyandrographolide CAS#:79233-15-1 |
| Literature: Fujita, Tetsuro; Fujitani, Ryujiro; Takeda, Yoshio; Takaishi, Yoshihisa; Yamada, Toshihide; et al Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1984 , vol. 32, # 6 p. 2117 - 2125 |
|
~% 
Deoxyandrographolide CAS#:79233-15-1 |
| Literature: Fujita, Tetsuro; Fujitani, Ryujiro; Takeda, Yoshio; Takaishi, Yoshihisa; Yamada, Toshihide; et al Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1984 , vol. 32, # 6 p. 2117 - 2125 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| Deoxyandrographolide |
| 2(5H)-Furanone, 3-[2-[(4aS,5R,6R,8aR)-3,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5,8a-trimethyl-1-naphthalenyl]ethyl]- |
| iso-14-deoxyandrographolide |
| 3-{2-[(4aS,5R,6R,8aR)-6-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5,8a-trimethyl-3,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydronaphthalen-1-yl]ethyl}furan-2(5H)-one |
| 3-{2-[(4aS,5R,6R,8aR)-6-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5,8a-trimethyl-3,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1-naphthalenyl]ethyl}-2(5H)-furanone |