Tiglic acid
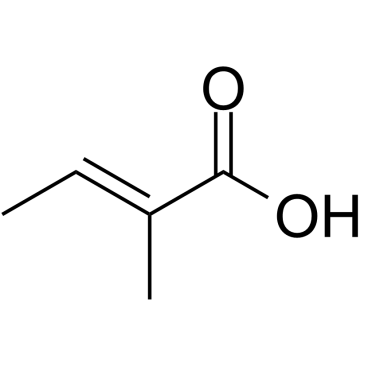
Tiglic acid structure
|
Common Name | Tiglic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 80-59-1 | Molecular Weight | 100.116 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 198.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O2 | Melting Point | 61-64 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 95.9±9.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Tiglic acidTiglic acid is a monocarboxylic unsaturated organic acid found in croton oil and in several other natural products. Tiglic aci has a role as a plant metabolite[1]. |
| Name | tiglic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Tiglic acid is a monocarboxylic unsaturated organic acid found in croton oil and in several other natural products. Tiglic aci has a role as a plant metabolite[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 198.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 61-64 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 100.116 |
| Flash Point | 95.9±9.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 100.052429 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 1.35 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.2±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.451 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator (+4°C) |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE IN HOT WATER |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H314 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 3261 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | GQ5430000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 29161980 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 29161980 |
|---|
|
Largamides A-C, tiglic acid-containing cyclodepsipeptides with elastase-inhibitory activity from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya confervoides.
Planta Med. 75 , 528-33, (2009) Three unusual tiglic acid-containing cyclodepsipeptides, possessing the revised regioisomeric structures for largamides A-C (1-3), have been isolated from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya confervoide... |
|
|
Pathway of formation of branched-chain volatile fatty acids in Ascaris mitochondria.
J. Parasitol. 67(6) , 841-6, (1981) Disrupted Ascaris mitochondria formed 2-methylbutyrate (2-MB) and 2-methylvalerate (2-MV) when incubated anaerobically with acetyl CoA, propionyl CoA and NADH. However, when mitochondrial membranes we... |
|
|
Biosynthesis of tiglic, ethacrylic, and 2-methylbutyric acids in a carabid beetle, Pterostichus (Hypherpes) californicus.
J. Chem. Ecol. 33(5) , 963-70, (2007) Tiglic, 2-methylbutyric, and ethacrylic acids are found in the pygidial gland defensive fluid of many carabid beetles. By injecting a deuterium-labeled precursor into the carabid beetle Pterostichus (... |
| (2E)-2-Methyl-2-butenoic acid |
| 2-Butenoic acid, 2-methyl-, (2E)- |
| FEMA 3599 |
| 2,3-Dimethylacrylic acid |
| EINECS 201-295-0 |
| (2E)-2-Methylbut-2-enoic acid |
| Cevadic acid |
| Tiglic acid |
| E-Tiglic acid |
| MFCD00066864 |
| Tiglate |
| (E)-2-methyl-2-butenoic acid |
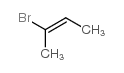 CAS#:3017-71-8
CAS#:3017-71-8 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2 CAS#:30574-97-1
CAS#:30574-97-1 CAS#:3017-68-3
CAS#:3017-68-3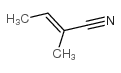 CAS#:4403-61-6
CAS#:4403-61-6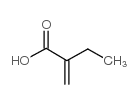 CAS#:3586-58-1
CAS#:3586-58-1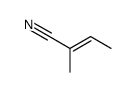 CAS#:20068-02-4
CAS#:20068-02-4 CAS#:55449-44-0
CAS#:55449-44-0 CAS#:10307-60-5
CAS#:10307-60-5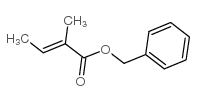 CAS#:37526-88-8
CAS#:37526-88-8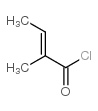 CAS#:35660-94-7
CAS#:35660-94-7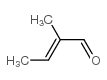 CAS#:497-03-0
CAS#:497-03-0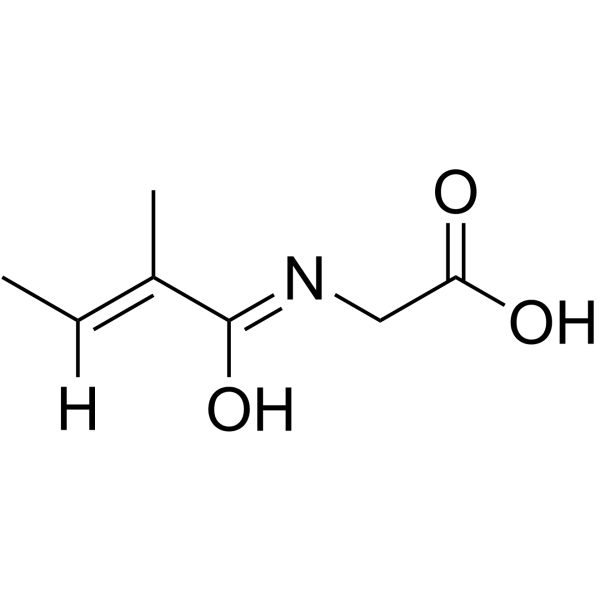 CAS#:35842-45-6
CAS#:35842-45-6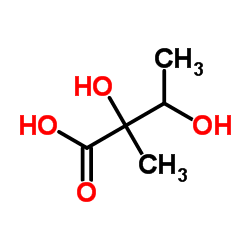 CAS#:14868-24-7
CAS#:14868-24-7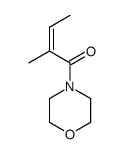 CAS#:212518-27-9
CAS#:212518-27-9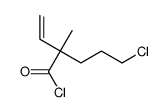 CAS#:193818-73-4
CAS#:193818-73-4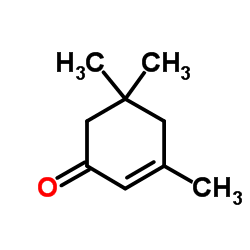 CAS#:78-59-1
CAS#:78-59-1
