Echinacoside
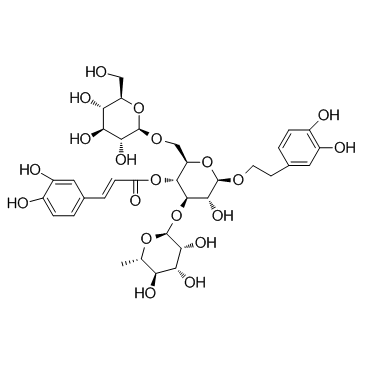
Echinacoside structure
|
Common Name | Echinacoside | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 82854-37-3 | Molecular Weight | 786.728 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1062.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C35H46O20 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 327.9±27.8 °C | |
Use of EchinacosideEchinacoside is a natural polyphenolic compound, has various kinds of pharmacological activities, such as antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, nitric oxide radical-scavenging and vasodilative ones.IC50 value:Target:in vitro: Echinacoside(ECH) dose dependently inhibited HEWL aggregation, and this inhibition occurred in different fiber-forming stages. ECH could also scavenge the DPPH and OH free radicals in a concentration-dependent manner. ECH could increase viability of rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells injured by Aβ and suppress the increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) triggered by Aβ [1]. Transient treatment with echinacoside inhibits cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activation caused by ensuing rotenone exposure via activating Trk-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway in neuronal cells [2]. ECH caused a significant increase in cell proliferation, ALP activity, COL I contents, OCN levels and an enhancement of mineralization in osteoblasts at the concentration range from 0.01 to 10nmol·L(-1) (p<0.05), suggesting that ECH has a stimulatory effect on osteoblastic bone formation or has potential activity against osteoporosis [4]. in vivo: In OVX rats, the increases of body weight, serum hydroxyproline (HOP) levels, and the decreases of uterus wet weight and BMD were significantly reversed by ECH treatment [3]. Echinacoside (60 mg/kg) was given intraperitoneally to mice at 1 h prior to GalN/LPS exposure. Pretreatment with echinacoside remarkably improved the survival rate of GalN/LPS-treated mice and attenuated acute hepatotoxicity, as demonstrated by decreased ALT levels and improved histological signs. Echinacoside shows both anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties, characterized by a substantial inhibition of hepatocyte apoptosis and a significant reduction in the inflammatory markers, including myeloperoxidase, extracellular nucleosomes, high-mobility group box 1, and inflammatory cytokines in the plasma of mice, which may be important mechanisms related to its protective effect [5]. |
| Name | [(2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-6-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-5-hydroxy-2-[[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]-4-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-3-yl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Echinacoside is a natural polyphenolic compound, has various kinds of pharmacological activities, such as antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, nitric oxide radical-scavenging and vasodilative ones.IC50 value:Target:in vitro: Echinacoside(ECH) dose dependently inhibited HEWL aggregation, and this inhibition occurred in different fiber-forming stages. ECH could also scavenge the DPPH and OH free radicals in a concentration-dependent manner. ECH could increase viability of rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells injured by Aβ and suppress the increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) triggered by Aβ [1]. Transient treatment with echinacoside inhibits cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activation caused by ensuing rotenone exposure via activating Trk-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway in neuronal cells [2]. ECH caused a significant increase in cell proliferation, ALP activity, COL I contents, OCN levels and an enhancement of mineralization in osteoblasts at the concentration range from 0.01 to 10nmol·L(-1) (p<0.05), suggesting that ECH has a stimulatory effect on osteoblastic bone formation or has potential activity against osteoporosis [4]. in vivo: In OVX rats, the increases of body weight, serum hydroxyproline (HOP) levels, and the decreases of uterus wet weight and BMD were significantly reversed by ECH treatment [3]. Echinacoside (60 mg/kg) was given intraperitoneally to mice at 1 h prior to GalN/LPS exposure. Pretreatment with echinacoside remarkably improved the survival rate of GalN/LPS-treated mice and attenuated acute hepatotoxicity, as demonstrated by decreased ALT levels and improved histological signs. Echinacoside shows both anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties, characterized by a substantial inhibition of hepatocyte apoptosis and a significant reduction in the inflammatory markers, including myeloperoxidase, extracellular nucleosomes, high-mobility group box 1, and inflammatory cytokines in the plasma of mice, which may be important mechanisms related to its protective effect [5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1062.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C35H46O20 |
| Molecular Weight | 786.728 |
| Flash Point | 327.9±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 786.258240 |
| PSA | 324.44000 |
| LogP | 0.14 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.698 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
Plantago lanceolata L. water extract induces transition of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and increases tensile strength of healing skin wounds.
J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67(1) , 117-25, (2014) Although the exact underlying mechanisms are still unknown, Plantago lanceolata L. (PL) water extracts are frequently used to stimulate wound healing and to drain abscesses. Therefore, in this experim... |
|
|
Echinacoside Induces Apoptosis in Human SW480 Colorectal Cancer Cells by Induction of Oxidative DNA Damages.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 14655-68, (2015) Echinacoside is a natural compound with potent reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging and anti-oxidative bioactivities, which protect cells from oxidative damages. As cancer cells are often under in... |
|
|
Echinacoside induces apoptotic cancer cell death by inhibiting the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme MTH1.
Onco. Targets Ther. 8 , 3649-64, (2015) Inhibition of the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme MTH1 causes extensive oxidative DNA damages and apoptosis in cancer cells and hence may be used as an anticancer strategy. As natural products have ... |
| (2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-6-[2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-5-hydroxy-2-({[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}methyl)-4-{[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl (2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acrylate |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->3)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)]-4-O-[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1-3)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-6)]-4-O-[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->3)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)]-4-O-[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl O-6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->3)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)]-4-O-[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl]- |
| β-D-glucopyranoside, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl O-6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->3)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)]-4-O-[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl]- |
| Echinacoside |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl-(1->3)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)]-4-O-[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| UNII-I04O1DT48T |

