Voglibose
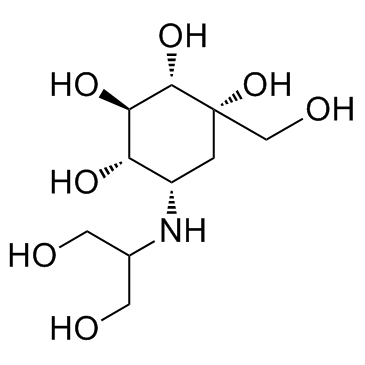
Voglibose structure
|
Common Name | Voglibose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 83480-29-9 | Molecular Weight | 267.276 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 601.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H21NO7 | Melting Point | 162-163ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 274.1±22.1 °C | |
Use of VogliboseVoglibose is an N-substituted derivative of valiolamine, excellent inhibitory activity against α-glucosidases and its action against hyperglycemia and various disorders caused by hyperglycemia.Target: α-glucosidasesglibose can inhibit the intestinal α-glucosidases, which are responsible for the digestion of disaccharides such as maltose and sucrose, including maltase and sucrase. The Ki values of Voglibose for sucrase and maltase are about 106and 105 times smaller than the Km values for sucrose and maltose [1]. Voglibose (0.2 mg/kg) completely inhibits the insulin response to sucrose in rats. Voglibose (0.2 mg/kg) reduces the carbohydrate-induced increase in blood glucose in rats. Voglibose (0.2 mg/kg) reduces the carbohydrate-induced increase in blood glucose without causing sustained hypoglycemia in both normal and neonatal streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats [2]. Voglibose (0.001%) treatment increases GLP-1 secretion (Voglibose alone, 1.6-fold; Alogliptin plus Voglibose, 1.5-fold), while it decreases plasma glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) (Voglibose alone, 30%; Alogliptin plus voglibose, 29%) in prediabetic db/db mice after 3 weeks. Voglibose (0.001%) treatment decreases plasma DPP-4 activity by 15% in prediabetic db/db mice. Voglibose (0.001%) treatment increases plasma insulin by 1.8-fold and decreases plasma glucagon by 8% in prediabetic db/db mice [3]. |
| Name | Voglibose |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Voglibose is an N-substituted derivative of valiolamine, excellent inhibitory activity against α-glucosidases and its action against hyperglycemia and various disorders caused by hyperglycemia.Target: α-glucosidasesglibose can inhibit the intestinal α-glucosidases, which are responsible for the digestion of disaccharides such as maltose and sucrose, including maltase and sucrase. The Ki values of Voglibose for sucrase and maltase are about 106and 105 times smaller than the Km values for sucrose and maltose [1]. Voglibose (0.2 mg/kg) completely inhibits the insulin response to sucrose in rats. Voglibose (0.2 mg/kg) reduces the carbohydrate-induced increase in blood glucose in rats. Voglibose (0.2 mg/kg) reduces the carbohydrate-induced increase in blood glucose without causing sustained hypoglycemia in both normal and neonatal streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats [2]. Voglibose (0.001%) treatment increases GLP-1 secretion (Voglibose alone, 1.6-fold; Alogliptin plus Voglibose, 1.5-fold), while it decreases plasma glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) (Voglibose alone, 30%; Alogliptin plus voglibose, 29%) in prediabetic db/db mice after 3 weeks. Voglibose (0.001%) treatment decreases plasma DPP-4 activity by 15% in prediabetic db/db mice. Voglibose (0.001%) treatment increases plasma insulin by 1.8-fold and decreases plasma glucagon by 8% in prediabetic db/db mice [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 601.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 162-163ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H21NO7 |
| Molecular Weight | 267.276 |
| Flash Point | 274.1±22.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 267.131805 |
| PSA | 153.64000 |
| LogP | -2.36 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.636 |
| Storage condition | Store at -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | NM7524600 |
|
~91% 
Voglibose CAS#:83480-29-9 |
| Literature: Fukase; Horii Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1992 , vol. 57, # 13 p. 3651 - 3658 |
|
~80% 
Voglibose CAS#:83480-29-9 |
| Literature: Ji, Li; Zhang, Ding-Feng; Zhao, Qian; Hu, San-Ming; Qian, Chao; Chen, Xin-Zhi Tetrahedron, 2013 , vol. 69, # 34 p. 7031 - 7037 |
|
~% 
Voglibose CAS#:83480-29-9 |
| Literature: WO2005/30698 A1, ; Page/Page column 9-10 ; |
|
~% 
Voglibose CAS#:83480-29-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 57, # 13 p. 3651 - 3658 |
|
Intensive glucose lowering in cardiovascular risk management - unsolved questions - .
Circ. J. 76(3) , 593-5, (2012)
|
|
|
Effects of voglibose and nateglinide on glycemic status and coronary atherosclerosis in early-stage diabetic patients.
Circ. J. 76(3) , 712-20, (2012) Postprandial hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia have been considered as important determinants for the development of atherosclerosis. However, it remains to be elucidated whether correction of the po... |
|
|
Effect of voglibose on the pharmacokinetics of metformin in healthy Korean subjects.
Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 52(11) , 1005-11, (2014) The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of voglibose on the pharmacokinetics of metformin.A randomized, open-label, two-way crossover study with a 7-day washout period was conducted. A... |
| Beigrace |
| Jumeal |
| Voglibose |
| Glustat |
| (1S,2S,3R,4S,5S)-5-[(1,3-Dihydroxy-2-propanyl)amino]-1-(hydroxymethyl)-1,2,3,4-cyclohexanetetrol |
| Voglibose (JP15/USAN) |
| Basen |
| Voglistat |
| 3,4-Dideoxy-4-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]amino]-2-C-(hydroxymethyl)-D-epiinositol |
| AO 128 |
| MFCD00865496 |
| 1,2,3,4-Cyclohexanetetrol, 5-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]amino]-1-(hydroxymethyl)-, (1S,2S,3R,4S,5S)- |
| (1S,2S,3R,4S,5S)-5-[(1,3-Dihydroxypropan-2-yl)amino]-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetrol |
| (1S,2S,3R,4S,5S)-5-{[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]amino}-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetrol |
| N-(1,3-Dihydroxy-2-propyl)valiolamine |
| (1S,2S,3R,4S,5S)-5-[(1,3-Dihydroxypropan-2-yl)amino]-1-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexan-1,2,3,4-tetrol |

![(2R,3S,4S,5S)-5-Hydroxy-2,3,4-tris(phenylmethoxy)-5-[(phenylmethoxy)methyl]-cyclohexanone structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/118/115250-38-9.png)

