Pyrogallol

Pyrogallol structure
|
Common Name | Pyrogallol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 87-66-1 | Molecular Weight | 126.110 | |
| Density | 1.453 | Boiling Point | 309 ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6O3 | Melting Point | 131-135 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 164.3±16.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of PyrogallolPyrogallol is a polyphenol compound, which has anti-fungal and anti-psoriatic properties. Pyrogallol is a reductant that is able to generate free radicals, in particular superoxide anions. |
| Name | Pyrogallol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pyrogallol is a polyphenol compound, which has anti-fungal and anti-psoriatic properties. Pyrogallol is a reductant that is able to generate free radicals, in particular superoxide anions. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Pyrogallol (PG) is a reductant that is able to generate free radicals, in particular superoxide anions (O2•-), so has frequently been used as a photographic developing agent and in the hair dying industry. Pyrogallol inhibits Calu-6 and A549 lung cancer cell growth via apoptosis and depletion of glutathione (GSH). Pyrogallol (PG) induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells via the overproduction of O2•- and affects mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in these cells[1]. The effect of Pyrogallol on human pulmonary fibroblast (HPF) cell viability and necrotic cell death is examined. For these experiments, 0, 50 or 100 µM Pyrogallol is used to differentiate the levels of cell viability inhibition or death with or without a given MAPK inhibitor. Treatment with 50 and 100 µM Pyrogallol decreases HPF viability by ~40 and 65% at 24 h, respectively. Treatment with an MEK inhibitor slightly enhances the inhibition of cell viability in 50 µM Pyrogallol-treated HPF cells, whereas treatment with a p38 inhibitor mildly attenuates the inhibition of viability. In 100 µM Pyrogallol-treated HPF cells, all the MAPK inhibitors increase the inhibition of viability to a certain extent, with treatment with the p38 inhibitor alone augmenting HPF control cell viability. Necrotic cell death is determined by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release from cells. While treatment with 50 µM Pyrogallol does not affect LDH release from HPF cells, 100 µM Pyrogallol significantly increases LDH release[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Briefly, 5×103 HPF cells per well in 96-well microtiter plates are exposed to 0, 50 or 100 µM Pyrogallol with or without each MAPK inhibitor at 37°C for 24 h. Changes in cell viability induced by Pyrogallol and/or a given MAPK inhibitor are determined by measuring the MTT; dye absorbance[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.453 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 309 ºC |
| Melting Point | 131-135 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 126.110 |
| Flash Point | 164.3±16.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 126.031693 |
| PSA | 60.69000 |
| LogP | 0.29 |
| Vapour density | 4.4 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.677 |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at RT |
| Stability | Stability Stable, but decolourises in light. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidising agents, alkalies, metal oxides, ammonia, antipyrine, phenol, iodine, lime water, menthol, potassium permanganate, strong bases. |
| Water Solubility | 400 g/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H341-H412 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22;R52/53;R68 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25-S61-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UX2800000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2907299090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2907299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2907299090 polyphenols; phenol-alcohols。supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:5.5%。general tariff:30.0% |
|
Biotransformation and nitroglycerin-induced effects on antioxidative defense system in rat erythrocytes and reticulocytes.
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 33(4) , 393-401, (2014) The effects of nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate - GTN) are mediated by liberated nitric oxide (NO) and formed reactive nitrogen species, which induces oxidative stress during biotransformation in re... |
|
|
Degradation of anti-inflammatory drug ketoprofen by electro-oxidation: comparison of electro-Fenton and anodic oxidation processes.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 21(14) , 8406-16, (2014) The electrochemical degradation of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug ketoprofen in tap water has been studied using electro-Fenton (EF) and anodic oxidation (AO) processes with platinium (Pt) an... |
|
|
Characterization of arsenic-induced cytotoxicity in liver with stress in erythrocytes and its reversibility with Pleurotus florida lectin.
Toxicol. Ind. Health 31(2) , 108-22, (2015) Arsenic is one of the most hazardous substances in the environment known to cause toxicity in multiple organs. Cell adhesion, morphological alterations, cell proliferation, terminal deoxyuridine triph... |
| 1,2,3-trishydroxybenzene |
| trihydroxybenzene |
| 1,2,3-Trihydroxybenzene |
| EINECS 201-762-9 |
| Pyrogallol |
| PYROGALL |
| MFCD00008358 |
| benzene-1,2,3-triol |
| Fourrine 85 |
| Benzol-1,2,3-triol |
| pyrogallic |
| 1,2,3-Benzenetriol |
| gallol |
| Piral |
| 1,2,3-trihydroxy-benzene |
| Fourrine PG |
| Phloroglucinol Impurity 1 |
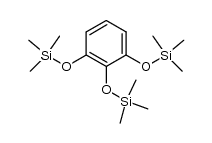 CAS#:17864-23-2
CAS#:17864-23-2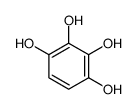 CAS#:642-96-6
CAS#:642-96-6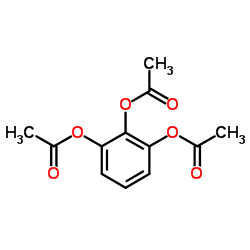 CAS#:525-52-0
CAS#:525-52-0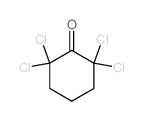 CAS#:3776-30-5
CAS#:3776-30-5 CAS#:91-10-1
CAS#:91-10-1 CAS#:634-36-6
CAS#:634-36-6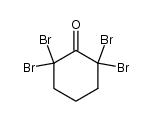 CAS#:29170-71-6
CAS#:29170-71-6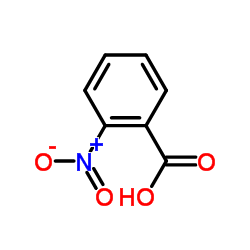 CAS#:552-16-9
CAS#:552-16-9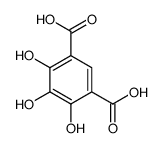 CAS#:27163-60-6
CAS#:27163-60-6![4-(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)spiro[1,3-benzodioxole-2,1'-cyclohexane] structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/294/106835-64-7.png) CAS#:106835-64-7
CAS#:106835-64-7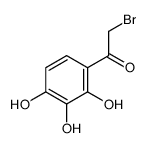 CAS#:105190-52-1
CAS#:105190-52-1 CAS#:38183-03-8
CAS#:38183-03-8 CAS#:486-35-1
CAS#:486-35-1 CAS#:32638-88-3
CAS#:32638-88-3 CAS#:528-21-2
CAS#:528-21-2 CAS#:92379-42-5
CAS#:92379-42-5 CAS#:35896-58-3
CAS#:35896-58-3 CAS#:31127-54-5
CAS#:31127-54-5
