AST-1306
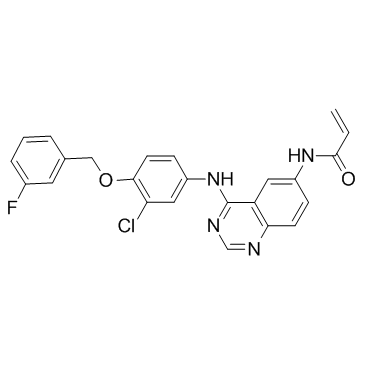
AST-1306 structure
|
Common Name | AST-1306 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 897383-62-9 | Molecular Weight | 448.877 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 655.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H18ClFN4O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 349.9±31.5 °C | |
Use of AST-1306AST1306 is a selective, irreversible EGFR and ErbB2 inhibitor with IC50s of 0.5 and 3 nM, respectively. |
| Name | N-[4-[3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]anilino]quinazolin-6-yl]prop-2-enamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | AST1306 is a selective, irreversible EGFR and ErbB2 inhibitor with IC50s of 0.5 and 3 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EGFR:0.5 nM (IC50) ErbB2:3 nM (IC50) EGFRL858R/T790M:12 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | AST1306 induces a significant, concentration-dependent inhibition of the growth of HIH3T3-EGFR T790M/L858R cells. In addition, AST1306 effectively inhibits EGFR phosphorylation in HIH3T3-EGFR T790M/L858R cells. AST1306 inhibits the growth of NCI-H1975 cells that harbor the EGFR T790M/L858R mutation in a concentration-dependent manner, and blocks phosphorylation of EGFR and downstream pathways as well. AST1306 inhibits the phosphorylation of EGFR and ErbB2, and downstream signaling in human cancer cells. AST1306 inhibits the proliferation of human cancer cells, with ErbB2-overexpressing cells exhibiting more sensitivity[1]. |
| In Vivo | AST1306 potently suppresses tumor growth in ErbB2-overexpressing adenocarcinoma xenograft and FVB-2/Nneu transgenic breast cancer mouse models, but weakly inhibits the growth of EGFR-overexpressing tumor xenografts. Tumor growth inhibition induced by a single dose of AST1306 in the SK-OV-3 xenograft model is accompanied by a rapid (within 2 h) and sustained (≥24 h) inhibition of both EGFR and ErbB2, consistent with an irreversible inhibition mechanism[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are seeded into 96-well plates and grown for 24 h. The cells are then treated with increasing concentrations of AST1306 and grown for a further 72 h. Cell proliferation is evaluated using the SRB (Sulforhodamine B) assay[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Mice are administered AST1306 at dosage of 100, 50 and 25 mg/kg twice daily and treated with lapatinib (50 mg/kg) as comparison. Tumors are measured twice a week in two dimensions, using a caliper, and the tumor volume is calculated according to the formula L×W×W/2[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 655.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C24H18ClFN4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 448.877 |
| Flash Point | 349.9±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 448.110229 |
| PSA | 79.63000 |
| LogP | 5.02 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.700 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~64% 
AST-1306 CAS#:897383-62-9 |
| Literature: EP1990337 A1, ; Page/Page column 9 ; |
|
~% 
AST-1306 CAS#:897383-62-9 |
| Literature: EP2292234 A1, ; |
|
~% 
AST-1306 CAS#:897383-62-9 |
| Literature: EP2292234 A1, ; |
|
~% 
AST-1306 CAS#:897383-62-9 |
| Literature: EP2292234 A1, ; |
| 2-Propenamide, N-[4-[[3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]amino]-6-quinazolinyl]- |
| cc-669 |
| AST 1306 |
| N-[4-({3-Chloro-4-[(3-fluorobenzyl)oxy]phenyl}amino)-6-quinazolinyl]acrylamide |
| QCR-149 |
| AST-1306 |
![N4-[3-chloro-4-(3-fluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-quinazoline-4,6-diamine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/427/845271-71-8.png)
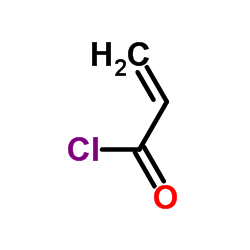
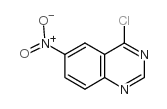
![3-Chloro-4-[(3-fluorobenzyl)oxy]aniline structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/081/202197-26-0.png)
![[3-chloro-4-(3-fluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(6-nitro-quinazolin-4-yl)-amine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/343/851653-35-5.png)