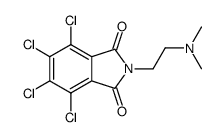
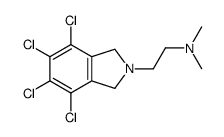
Chlorisondamine diiodide
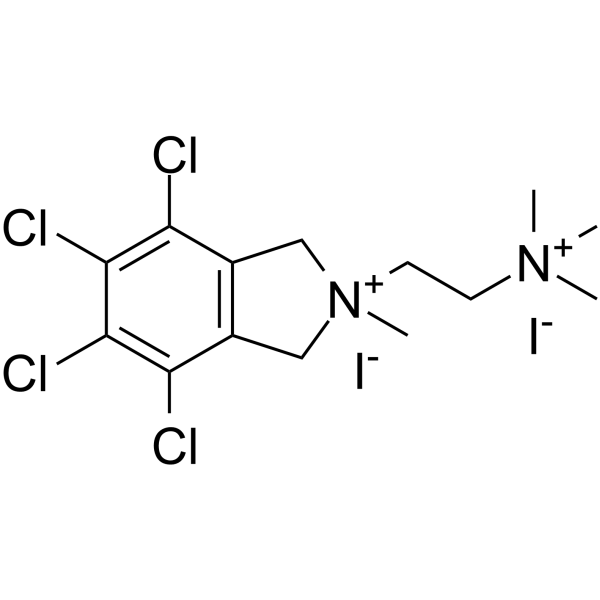
Chlorisondamine diiodide structure
|
Common Name | Chlorisondamine diiodide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 96750-66-2 | Molecular Weight | 611.94 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H20Cl4I2N2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Chlorisondamine diiodideChlorisondamine (diiodide) is a potent nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) antagonist and a ganglion blocker. Chlorisondamine antagonizes some of nicotine's central actions in a potent, long-lasting and pharmacologically selective way[1]. |
| Name | trimethyl-[2-(4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-2-methyl-1,3-dihydroisoindol-2-ium-2-yl)ethyl]azanium,diiodide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chlorisondamine (diiodide) is a potent nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) antagonist and a ganglion blocker. Chlorisondamine antagonizes some of nicotine's central actions in a potent, long-lasting and pharmacologically selective way[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
nAChR[1] |
| In Vivo | Chlorisondamine (0.2, 1.0, 5.0 μg; IV; single dosage) antagonizes the depressant action of nicotine on vertical activity (0-20min) in a dose-dependent way at 1 and 2 weeks[1]. Animal Model: Rats (treated once with nicotine 0.4 mg/kg, s.c.)[1] Dosage: 0.2, 1.0, 5.0 μg Administration: IV; single dosage Result: Antagonized the depressant action of nicotine on vertical activity (0-20min) in a dose-dependent way at 1 and 2 weeks. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C14H20Cl4I2N2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 611.94 |
| Exact Mass | 609.84700 |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H400 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful;N: Dangerous for the environment; |
| Risk Phrases | 22-50 |
| Safety Phrases | 60-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Cardiovascular afferents cause the release of 5-HT in the nucleus tractus solitarii; this release is regulated by the low- (PMAT) not the high-affinity transporter (SERT).
J. Physiol. 593(7) , 1715-29, (2015) The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) integrates inputs from cardiovascular afferents and thus is crucial for cardiovascular homeostasis. These afferents primarily release glutamate, although 5-HT has a... |
|
|
Effects of nicotine and chlorisondamine on cerebral glucose utilization in immobilized and freely-moving rats.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 129 , 147-155, (2000) Chlorisondamine blocks central nicotinic receptors for many weeks via an unknown mechanism. Intracerebroventricular administration of [(3)H]-chlorisondamine in rats results in an anatomically restrict... |
|
|
Modulation of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by halothane in rat cortical neurons.
Mol. Pharmacol. 59 , 732-743, (2001) Inhalational general anesthetics have recently been shown to inhibit neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptors (nnAChRs) expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes and in molluscan neurons. However, d... |
| 4,5,6,7-Tetrachlor-2-methyl-2-(2-trimethylammonio-aethyl)-isoindolinium,Dijodid |
| trimethyl-[2-[4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-2-(tritritiomethyl)-1,3-dihydroisoindol-2-ium-2-yl]ethyl]azanium |
| 4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-2-methyl-2-[2-(trimethylammonium)ethyl]isoindolinium diiodide |
| chlorisondamine iodide |
| 4,5,6,7-Tetrachloro-2,3-dihydro-2-methyl-2-[2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl]-2H-isoindolium diiodide |
| 4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-2-methyl-2-(2-trimethylammonio-ethyl)-isoindolinium,diiodide |