3-羟基苯乙酸
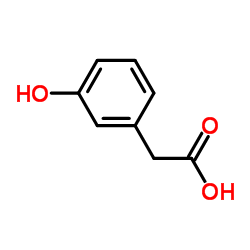
3-羟基苯乙酸结构式

|
常用名 | 3-羟基苯乙酸 | 英文名 | 3-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 621-37-4 | 分子量 | 152.147 | |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 349.0±17.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C8H8O3 | 熔点 | 129-133 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 179.1±17.4 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
A metabolite profiling approach to identify biomarkers of flavonoid intake in humans.
J. Nucl. Med. 139 , 2309-14, (2009) Flavonoids are phytochemicals that are widespread in the human diet. Despite limitations in their bioavailability, experimental and epidemiological data suggest health benefits of flavonoid consumption. Valid biomarkers of flavonoid intake may be useful for e... |
|
|
Development of a targeted method for twenty-three metabolites related to polyphenol gut microbial metabolism in biological samples, using SPE and UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS.
Talanta 128 , 221-30, (2014) An increasing number of studies have concerned the profiling of polyphenol microbial metabolites, especially in urine or plasma, but only a few have regarded their accurate quantification. This study reports on a new ultra-performance liquid chromatography ta... |
|
|
Sensitive and Rapid UHPLC-MS/MS for the Analysis of Tomato Phenolics in Human Biological Samples.
Molecules 20 , 20409-25, (2015) An UHPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of tomato phenolic metabolites in human fluids was optimized and validated, and then applied in a pilot dietary intervention study with healthy volunteers. A 5-fold gain in speed (3.5 min of total run); 7-fold incr... |
|
|
Lack of tissue accumulation of grape seed flavanols after daily long-term administration in healthy and cafeteria-diet obese rats.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 9996-10003, (2015) After ingestion flavanols are metabolized by phase-II enzymes and the microbiota and are distributed throughout the body depending on several factors. Herein we aim to evaluate whether flavanols are tissue-accumulated after the long-term administration of a g... |
|
|
Rapid diagnosis of phenylketonuria and other aminoacidemias by quantitative analysis of amino acids in neonatal blood spots by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 775(1) , 115-20, (2002) A new method for quantifying specific amino acids in small volumes of plasma and whole blood has been developed. Volatile derivatives of amino acids are analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method only takes a few minutes to perform and requi... |
|
|
The occurrence of gamma-glutamylphenylalanine in the urine of newborn phenylketonurics.
Clin. Chim. Acta 94(3) , 237-40, (1979) The urine of untreated phenylketonurics in the first weeks of life contains gamma-glutamylphenylalanine (0.07--0.69 mmol/g creatinine, 12 samples) visible on the normal 2-dimensional electrophoreto-chromatogram. This compound is less prominent or absent when ... |
|
|
Renal transport of aromatic acids in patients with phenylketonuria.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 4(2) , 69-70, (1981) Renal clearance of phenylpyruvic acid is maximal at a plasma concentration of 40-60 mumol/l. This concentration is obtained with plasma phenylalanine concentrations of 1.0-1.2 mmol/l, the threshold for separating classical phenylketonuria from phenylketonuria... |
|
|
Plasma concentrations of phenyllactic acid in phenylketonuria.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 13(2) , 227-8, (1990)
|
|
|
First ISNS Reference Preparation for Neonatal Screening for thyrotropin, phenylalanine and 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone in blood spots.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 30(4) , 609, (2007) Neonatal screening for congenital disorders like phenylketonuria (PKU), congenital hypothyroidism (CH) and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is generally performed in dried blood spots on filter paper. The analytes of interest for testing for PKU, CH and C... |
|
|
Mass spectrometric behavior of phenolic acids standards and their analysis in the plant samples with LC/ESI/MS system.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 967 , 21-7, (2014) Liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) with electrospray ionization (ESI) is one of analytical techniques to obtain accurate results of low molecular weight aromatic compounds in biological samples of different origin. The interpretations of ... |