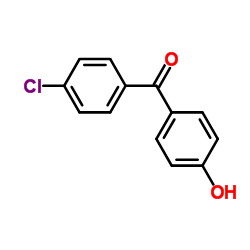
非诺贝特酸

非诺贝特酸结构式

|
常用名 | 非诺贝特酸 | 英文名 | Fenofibric acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 42017-89-0 | 分子量 | 318.752 | |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 486.5±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C17H15ClO4 | 熔点 | 176--179ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 248.0±25.9 °C | |
| 符号 |


GHS07, GHS09 |
信号词 | Warning |
非诺贝特酸用途Fenofibric acid 是 fenofibrate 的活性代谢物,为 PPAR 激动剂,对 PPARα,PPARγ 和 PPARδ 的 EC50 值分别为 22.4 µM,1.47 µM 和 1.06 µM;Fenofibric acid 同时可抑制 COX-2 的活性,IC50 值为 48 nM。 |
| 中文名 | 非诺贝特酸 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | fenofibric acid |
| 中文别名 | 2-(4-(4-氯苯甲酰)苯氧基)-2-甲基丙酸 | 非诺贝酸 | 2-[4-(4-氯苯甲酰基)苯氧基]-2-甲基丙酸 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Fenofibric acid 是 fenofibrate 的活性代谢物,为 PPAR 激动剂,对 PPARα,PPARγ 和 PPARδ 的 EC50 值分别为 22.4 µM,1.47 µM 和 1.06 µM;Fenofibric acid 同时可抑制 COX-2 的活性,IC50 值为 48 nM。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 靶点 |
PPARδ:1.06 μM (EC50) PPARγ:1.47 μM (EC50) PPARα:22.4 μM (EC50) COX-2:48 μM (IC50) |
| 体外研究 | Fenofibric acid是一种PPAR激活剂,PPARα,PPARγ和PPARδ的EC50分别为22.4μM,1.47μM和1.06μM[1]。非诺贝酸(10,25,50,75和100 nM)剂量依赖性地抑制COX-2酶,IC50为48 nM [2]。非诺贝酸(500 nM)可降低HepG2细胞中AOX1蛋白的丰度[3]。 Fenofibric acid(100μM)可降低JNK1/2,c-Jun和p38 MAPK的磷酸化水平,并可防止活性氧,内质网(ER)应激和血液视网膜屏障(BRB)破坏的积累。 ARPE-19细胞中的高葡萄糖(HG)和缺氧。在HG条件和缺氧条件下,非诺贝酸(100μM)激活ARPE-19细胞中IGF-IR/Akt/ERK1/2介导的存活信号通路[4]。 |
| 体内研究 | Fenofibric acid(1,5,10 mg/kg,po)在由角叉菜胶诱导的急性炎症的Wistar大鼠中显示出抗炎活性[2]。 |
| 细胞实验 | ARPE-19细胞在正常血糖(5.5mM D-葡萄糖)或高血糖(25mM D-葡萄糖)条件下在37℃,5%(v / v)CO 2下培养18天,培养基DMEM / F12补充10% (v / v)胎儿血清(FS)和青霉素/链霉素。使用ARPE-19细胞,每3-4天更换培养基。测试的条件是:(1)将对照细胞维持在5.5mM D-葡萄糖(正常葡萄糖)中18天。 (2)在用100μM非诺贝酸处理的5.5mM D-葡萄糖中培养72小时(第16,17和18天;每天施用1次)的细胞。 (3)如(1)或(2)中培养的细胞,并在最后6或24小时内进行缺氧(1%氧气)。 (4)细胞维持在25mM D-葡萄糖(HG)中18天。 (5)在用100μM非诺贝酸处理的25mM D-葡萄糖中培养72小时(第16,17和18天;每天施用1次)的细胞。 (6)如(4)或(5)中培养的细胞,在最后6或24小时内进行缺氧(1%氧气)[4]。 |
| 动物实验 | 通过将0.1mL在盐水(足底下)中制备的1%角叉菜胶溶液注射到大鼠的右后爪来评估非诺贝特及其活性代谢物fenofibric acid的抗炎活性。将大鼠分成6组,每组6只动物。第一组用作阴性对照,并在蒸馏水中接受1%吐温-80,10mL / kg体重。第2组和第3组接受单剂量非诺贝特和标准药物双氯芬酸10 mg / kg体重,而第4,5和6组分别接受3剂量的Fenofibric acid,分别为1,5和10 mg / kg体重。在通过足底下途径注射0.1mL的1%角叉菜胶之前60分钟使用管饲口服给予所有药物。在诱导炎症后0,1,2和3小时使用体积描记器测量测试组和对照组的水肿体积[2]。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 486.5±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 176--179ºC |
| 分子式 | C17H15ClO4 |
| 分子量 | 318.752 |
| 闪点 | 248.0±25.9 °C |
| 精确质量 | 318.065887 |
| PSA | 63.60000 |
| LogP | 3.86 |
| 外观性状 | 白色或近乎于白色结晶粉末 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.585 |
| 储存条件 | -20°C Freezer |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):无 2.氢键供体数量:1 3.氢键受体数量:4 4.可旋转化学键数量:5 5.互变异构体数量:无 6.拓扑分子极性表面积:63.6 7.重原子数量:22 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:405 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 符号 |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Warning |
| 危害声明 | H302-H410 |
| 警示性声明 | P273-P501 |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xn,N |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R36/37/38 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | 26-36/37/39 |
| 危险品运输编码 | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| RTECS号 | UA2453000 |
| 海关编码 | 2918990090 |
|
~93% 
非诺贝特酸 42017-89-0 |
| 文献:AMPLA PHARMACEUTICALS INC. Patent: WO2009/73138 A2, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 81-82 ; WO 2009/073138 A2 |
|
~72% 
非诺贝特酸 42017-89-0 |
| 文献:SIGNATURE PHARMACEUTICALS, LLC Patent: WO2005/46575 A2, 2005 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 176-177 ; |
|
~86% 
非诺贝特酸 42017-89-0 |
| 文献:Davis, Roman D.; Fitzgerald, Russ N.; Guo, Jiasheng Synthesis, 2004 , # 12 p. 1959 - 1962 |
|
~98% 
非诺贝特酸 42017-89-0 |
| 文献:Mattsson, Sara; Dahlstroem, Mikael; Karlsson, Staffan Tetrahedron Letters, 2007 , vol. 48, # 14 p. 2497 - 2499 |
|
~% 
非诺贝特酸 42017-89-0 |
| 文献:Labor. Fournier Patent: FR2300552DE2605382 , 19761976 ; Chem.Abstr., 1976 , vol. 85, # 192382 |
|
~% 
非诺贝特酸 42017-89-0 |
| 文献:Labor. Fournier Patent: FR2300552DE2605382 , 19761976 ; Chem.Abstr., 1976 , vol. 85, # 192382 |
| 海关编码 | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| 中文概述 | 2918990090. 其他含其他附加含氧基羧酸(包括酸酐、酰卤化物、过氧化物和过氧酸及该税号的衍生物). 增值税率:17.0%. 退税率:13.0%. 监管条件:无. 最惠国关税:6.5%. 普通关税:30.0% |
| 申报要素 | 品名, 成分含量, 用途 |
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Enzymatic characterization of ELOVL1, a key enzyme in very long-chain fatty acid synthesis.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1851(2) , 231-7, (2015) X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is a neurometabolic disease that is caused by mutations in the ABCD1 gene. ABCD1 protein deficiency impairs peroxisomal very long-chain fatty acid (VLCFA) degrada... |
|
|
The Lidose hard capsule formulation of fenofibrate is suprabioavailable compared to the nanoparticle tablet formulation under high-fat fed conditions.
J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 18(1) , 61-7, (2015) The therapeutic equivalence of multiple registered fenofibrate formulations, several of which are suprabioavailable and therefore marketed at lower dosage strengths than their reference products, is b... |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum stress involved in high-fat diet and palmitic acid-induced vascular damages and fenofibrate intervention.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 458(1) , 1-7, (2015) Fenofibrate (FF) is widely used to lower blood lipids in clinical practice, but whether its protective effect on endothelium-dependent vasodilatation (EDV) in thoracic aorta is related with endoplasmi... |
| Procetofenic acid |
| 2-(4'-(p-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropionic acid |
| 2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid |
| Fibricor |
| Propanoic acid, 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl- |
| Fenofibric acid |
| Fenofibrate Related Compound B |
| 2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid |
| Fenofibrate impurity B |
| EINECS 255-626-9 |
| MFCD00792461 |
| 2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropionic acid |
| 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid |

![benzyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/130/1159999-13-9.png)


 CAS号856676-23-8
CAS号856676-23-8![propan-2-yl 2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)-hydroxymethyl]phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/398/61001-99-8.png) CAS号61001-99-8
CAS号61001-99-8![2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoyl chloride结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/055/65178-90-7.png) CAS号65178-90-7
CAS号65178-90-7
