古伦宾
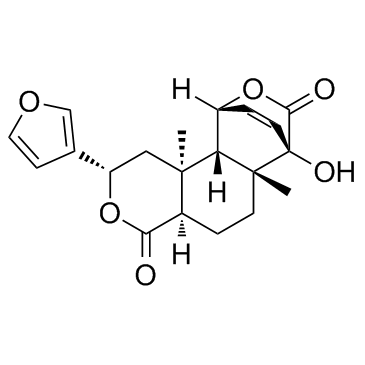
古伦宾结构式

|
常用名 | 古伦宾 | 英文名 | Columbin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 546-97-4 | 分子量 | 358.385 | |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 565.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C20H22O6 | 熔点 | 190-191ºC | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 296.0±30.1 °C |
古伦宾用途Columbin是具有抗炎活性的二萜类螺内酯。 |
| 中文名 | 古伦宾 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | (1R,2S,3S,5S,8R,11R,12R)-5-(3-Furyl)-12-hydroxy-3,11-dimethyl-6,14-dioxatetracyclo[10.2.2.02,11.03,8]hexadec-15-ene-7,13-dione |
| 中文别名 | 古伦宾,非洲防己苦素 | 非洲防己苦素 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Columbin是具有抗炎活性的二萜类螺内酯。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 体外研究 | 用columbin或l-NAME处理抑制LPS/IFN-γ诱导的NO产生而不影响RAW264.7的活力。用柯林蛋白预处理受刺激的细胞不会抑制LPS刺激的细胞中NF-κB向细胞核的转运。 columbin的COX-1和COX-2抑制活性在100μM时分别为63.7±6.4%和18.8±1.5%抑制。 columbin与Tyr385和Arg120的相互作用表明其在COX-2中具有更高的活性,因为据报道Tyr385参与从花生四烯酸的C-13中提取氢,而Arg120对于高亲和力的花生四烯酸结合至关重要[1]。 |
| 体内研究 | Columbin抑制小鼠爪子的水肿形成。在300mg/kg和700mg/kg的剂量下,columbin在0至5小时内抑制炎症,并且结果与作为标准抗炎药的阿司匹林的结果相当。 columbin对角叉菜胶诱导的小鼠足肿胀的抑制作用可能是由于抑制了包括前列腺素在内的炎症引起的介质的释放[1]。哥伦丁在大鼠中具有较差的生物利用度(2.8%po和14%ip),但其在Caco-2细胞单层中的运输速度很快,这表明肝脏中广泛的首过代谢可能是其生物利用度差的原因[2]。 。 |
| 动物实验 | 大鼠:雄性Wistar大鼠如下处理:静脉内注射columbin在EtOH和PEG-300(1:1)中通过尾静脉以20mg / kg的剂量给药。腹膜内(ip)注射columbin在EtOH和PEG-300(1:1)中的剂量为20mg / kg。口服管饲悬浮于口服悬浮载体中的columbin以50mg / kg的剂量给予大鼠。通过在0,5,15,30,45,60,120,240,360,480和1440分钟将尾巴剪入肝素化管中以静脉内施用或在0,15,收集血液样品(50-100μL),口服给药或腹腔注射30,60,120,180,240,360,480,1440分钟。将血液样品储存在-20℃直至分析[2]。小鼠:将雄性Balb / c小鼠(n = 60)随机分成六组。将Columbin以30,100,300和700mg / kg的剂量腹膜内给予小鼠。阿司匹林是一种抗炎药,用作阳性对照。为了在爪中诱导急性期炎症,在载体或columbin处理后30分钟,用1%溶解于盐水中的角叉菜胶溶液将大鼠皮下注射到右后爪中。在注射后5小时内以1小时的间隔测量爪体积。在注射角叉菜胶之前立即用体积描记器测量爪体积,然后以1小时的间隔测量5小时[1]。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 565.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 190-191ºC |
| 分子式 | C20H22O6 |
| 分子量 | 358.385 |
| 闪点 | 296.0±30.1 °C |
| 精确质量 | 358.141632 |
| PSA | 85.97000 |
| LogP | 0.58 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.593 |
| 储存条件 | -20°C |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
| 古伦宾上游产品 1 | |
|---|---|
| 古伦宾下游产品 1 | |
|
In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of columbin through the inhibition of cycloxygenase-2 and nitric oxide but not the suppression of NF-κB translocation.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 678(1-3) , 61-70, (2012) Columbin, a diterpenoid furanolactone, was isolated purely for the first time from the plant species Tinspora bakis. The anti-inflammatory effects of columbin were studied in vitro, in silico and in v... |
|
|
A bitter diterpenoid furanolactone columbin from Calumbae Radix inhibits azoxymethane-induced rat colon carcinogenesis.
Cancer Lett. 183(2) , 131-9, (2002) The modifying effect of dietary administration of a diterpenoid furanolactone columbin isolated from the crude drug Calumbae Radix (the root of Jateorhiza columba MIERS, Menispermacea) on azoxymethane... |
|
|
Inhibition of Naja nigricolis venom acidic phospholipase A2 catalysed hydrolysis of ghost red blood cells by columbin.
J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 17(1) , 55-9, (2002) The inhibitory effects of a naturally occurring diterpenoid furanolactone, columbin, on partially purified acidic phospholipase A2 (PLA2) from Naja nigricolis was investigated. Columbin inhibited the ... |
| (1R,2S,3S,5S,8R,11R,12R)-5-(3-Furyl)-12-hydroxy-3,11-dimethyl-6,14-dioxatetracyclo[10.2.2.0.0]hexadec-15-ene-7,13-dione |
| 15,16-Epoxy-1b,4,12-trihydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-17,18-dinor-8bH,9bH,10a-labda-2,13(16),14-triene-19,20-dioic Acid 19,1:20,12-Dilactone |
| 1,4-Etheno-3H,7H-benzo[1,2-c:3,4-c']dipyran-3,7-dione, 9-(3-furanyl)-1,4,4a,5,6,6a,9,10,10a,10b-decahydro-4-hydroxy-4a,10a-dimethyl-, (1R,4R,4aR,6aR,9S,10aS,10bS)- |
| (2S,4aR,6aR,7R,10R,10aS,10bS)-2-(furan-3-yl)-7-hydroxy-6a,10b-dimethyl-1,2,4a,5,6,6a,7,10,10a,10b-decahydro-4H-10,7-(epoxymethano)benzo[f]isochromene-4,12-dione |
| Columbin |

![2-(furan-3-yl)-6a,10b-dimethyl-4,12-dioxo-1,4a,5,6,6a,10,10a,10b-octahydro-2h-10,7-(epoxymethano)benzo[f]isochromen-7(4h)-yl hexopyranoside结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/212/105597-94-2.png)
 CAS号471-54-5
CAS号471-54-5
