凝乳酶
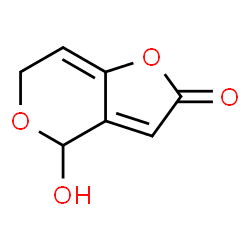
凝乳酶结构式

|
常用名 | 凝乳酶 | 英文名 | Rennin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 9001-98-3 | 分子量 | 154.120 | |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 513.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C7H6O4 | 熔点 | 225-227℃ | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 226.8±23.6 °C | |
| 符号 |


GHS07, GHS08 |
信号词 | Danger |
凝乳酶用途肾素,又称凝乳酶,是一种胃蛋白酶相关的蛋白水解酶,由某些动物胃内的细胞合成,能有效地将液态奶转化为半固体,使其在胃内停留更长时间。肾素的天然底物是K酪蛋白,它在氨基酸残基105和106、苯丙氨酸和蛋氨酸之间的肽键处被特异性切割,广泛用于奶酪生产[1]。 |
| 中文名 | 凝乳酶 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | Rennin |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | 肾素,又称凝乳酶,是一种胃蛋白酶相关的蛋白水解酶,由某些动物胃内的细胞合成,能有效地将液态奶转化为半固体,使其在胃内停留更长时间。肾素的天然底物是K酪蛋白,它在氨基酸残基105和106、苯丙氨酸和蛋氨酸之间的肽键处被特异性切割,广泛用于奶酪生产[1]。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 513.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 225-227℃ |
| 分子式 | C7H6O4 |
| 分子量 | 154.120 |
| 闪点 | 226.8±23.6 °C |
| 精确质量 | 154.026611 |
| LogP | -0.75 |
| 外观性状 | 固体 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.603 |
| 储存条件 | -20°C,密闭,避光,通风干燥处 |
| 稳定性 | 一种含硫的特殊蛋白酶。等电点pH值为4.5,干燥物活性稳定,但水溶液不稳定。水溶液的pH值约为37~43℃,在15℃以下、55℃以上时呈非活性。商品凝乳酶1g加入10升牛奶中,在35℃下可在40min内凝固。所含主要作用酶为蛋白酶,主要作为多肽类的水解,尤其是胃蛋白酶难以水解者。 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:微黄色冻干粉末或粒状、鳞片状。取自小牛胃。 2. 密度(g/mL,25/4℃): 未确定
3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):未确定 4. 熔点(ºC):未确定 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):未确定 6. 沸点(ºC,5.2kPa):未确定 7. 折射率:未确定 8. 闪点(ºC): 未确定 9. 比旋光度(º):未确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):未确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):未确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):未确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):未确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):未确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):未确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:未确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):未确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):未确定 19. 溶解性:部分溶于水、稀乙醇。在接近等电点p14.5时不溶解。 |
| 符号 |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Danger |
| 危害声明 | H315-H319-H334-H335 |
| 警示性声明 | P261-P305 + P351 + P338-P342 + P311 |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | B,Xn |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | 36/37/38-42 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | 22-24-26-36/37 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK德国 | 1 |
1.小牛、小山羊或羊羔(亦可由牛、绵羊城或山羊)第四胃(皱胃)的水抽提液。一般经水洗、干燥、切片后在4%硼酸水溶液中于30℃下浸渍5天抽提而得,或用食盐浸出后干燥而成。
2.蜡状芽孢杆菌(Bacillus cereus)、栗疫菌(Endot.hia parasitica)的非致病菌菌种或毛霉(Mucormiehei)或微小毛霉(M.pusillus)在受控条件下发酵产生。
|
Proteomic profiling of the coagulation of milk proteins induced by chymosin.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(8) , 2039-45, (2012) Chymosin-induced coagulation of individual milk proteins during incubation at 30 °C was investigated using a proteomic approach. The addition of chymosin (0.006 units/mL) caused the milk proteins to c... |
|
|
Starch addition in renneted milk gels: Partitioning between curd and whey and effect on curd syneresis and gel microstructure
J. Dairy Sci. 95(12) , 6871-81, (2012) Milk gels were made by renneting and acidifying skim milk containing 5 different starches, and then compressed by centrifugation to express whey and simulate curd syneresis during the manufacture of l... |
|
|
Constitutive expression, purification and characterization of bovine prochymosin in Pichia pastoris GS115.
World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28(5) , 2087-93, (2012) Chymosin can specifically break down the Phe105-Met106 peptide bond of milk κ-casein to form insoluble para-κ-casein, resulting in milk coagulation, a process that is used in making cheese. In this st... |
| EINECS 232-645-0 |
| MFCD00132173 |


