L-Threonine
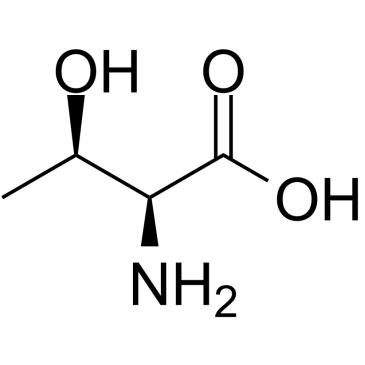
L-Threonine structure
|
Common Name | L-Threonine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 72-19-5 | Molecular Weight | 119.119 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 345.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO3 | Melting Point | 255ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 162.9±25.1 °C | |
|
Urinary metabolic fingerprinting of mice with diet-induced metabolic derangements by parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive gas chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1361 , 265-76, (2014) This study investigates the potential of a parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive GC platform (GC×2GC-MS/FID) for metabolic profiling and fingerprinting of mouse urine. Samples were obtained from a murine model that mimics... |
|
|
Mechanism of chemical activation of sodium chloride in the presence of amino acids.
Food Chem. 166 , 301-8, (2014) Sodium chloride has been shown to promote chlorination of glycerol during thermal processing. However, the detailed mechanism of this reaction is not well understood. Preliminary experiments have indicated that the reaction mixture should contain an amino aci... |
|
|
The unique serine/threonine phosphatase from the minimal bacterium Mycoplasma synoviae: biochemical characterization and metal dependence.
J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 20(1) , 61-75, (2015) Serine/threonine protein phosphatases have been described in many pathogenic bacteria as essential enzymes involved in phosphorylation-dependent signal transduction pathways and frequently associated with the virulence of these organisms. An inspection of Myc... |
|
|
Silica-based nanofibers for electrospun ultra-thin layer chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1364 , 261-70, (2014) Nanofibrous silica-based stationary phases for electrospun ultra-thin layer chromatography (E-UTLC) are described. Nanofibers were produced by electrospinning a solution of silica nanoparticles dispersed in polyvinylpyrrolidone solutions to create composite s... |
|
|
Novel lectin-independent approach to detect galactose-deficient IgA1 in IgA nephropathy.
Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 30 , 1315-21, (2015) Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) is a critical effector molecule in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy (IgAN). Although many researchers have measured serum levels of Gd-IgA1 using snail helix aspersa agglutinin (HAA) lectin-based assay, the lectin-depende... |
|
|
Disentangling the Complexity of HGF Signaling by Combining Qualitative and Quantitative Modeling.
PLoS Comput. Biol. 11 , e1004192, (2015) Signaling pathways are characterized by crosstalk, feedback and feedforward mechanisms giving rise to highly complex and cell-context specific signaling networks. Dissecting the underlying relations is crucial to predict the impact of targeted perturbations. ... |
|
|
ATG16L1 phosphorylation is oppositely regulated by CSNK2/casein kinase 2 and PPP1/protein phosphatase 1 which determines the fate of cardiomyocytes during hypoxia/reoxygenation.
Autophagy 11 , 1308-25, (2015) Recent studies have shown that the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of ULK1 and ATG13 are related to autophagy activity. Although ATG16L1 is absolutely required for autophagy induction by affecting the formation of autophagosomes, the post-translational ... |
|
|
EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication (EGFR-KDD) Is a Novel Oncogenic Driver in Lung Cancer That Is Clinically Responsive to Afatinib.
Cancer Discov. 5 , 1155-63, (2015) Oncogenic EGFR mutations are found in 10% to 35% of lung adenocarcinomas. Such mutations, which present most commonly as small in-frame deletions in exon 19 or point mutations in exon 21 (L858R), confer sensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). In... |
|
|
Enhancement of innate immune system in monocot rice by transferring the dicotyledonous elongation factor Tu receptor EFR.
J. Integr. Plant Biol. 57 , 641-52, (2015) The elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) receptor (EFR) in cruciferous plants specifically recognizes the N-terminal acetylated elf18 region of bacterial EF-Tu and thereby activates plant immunity. It has been demonstrated that Arabidopsis EFR confers broad-spectrum ... |
|
|
Renal nerve stimulation leads to the activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 via angiotensin II type I receptor.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 308 , F848-56, (2015) Renal nerve stimulation at a low frequency (below 2 Hz) causes water and sodium reabsorption via α1-adrenoreceptor tubular activation, a process independent of changes in systemic blood pressure, renal blood flow, or glomerular filtration rate. However, the u... |