Prednicarbate
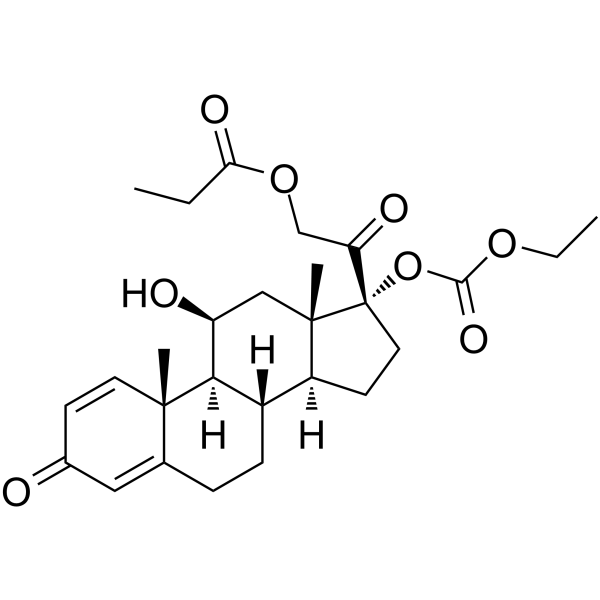
Prednicarbate structure
|
Common Name | Prednicarbate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73771-04-7 | Molecular Weight | 488.570 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 640.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H36O8 | Melting Point | 110 - 112ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 209.4±25.0 °C | |
|
Cetuximab-induced skin exanthema: prophylactic and reactive skin therapy are equally effective.
J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 139(10) , 1667-72, (2013) Treatment with cetuximab is accompanied by the development of an acneiform follicular skin exanthema in more than 80 % of patients. Severe exanthema (grade III/IV) develops in about 9-19 % of patients with the necessity of cetuximab dose reduction or cessatio... |
|
|
Drug release and skin penetration from solid lipid nanoparticles and a base cream: a systematic approach from a comparison of three glucocorticoids.
Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 24(4) , 199-209, (2011) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) can enhance drug penetration into the skin, yet the mechanism of the improved transport is not known in full. To unravel the influence of the drug-particle interaction on penetration enhancement, 3 glucocorticoids (GCs), predn... |
|
|
Efficacy of crisis intervention treatment with topical corticosteroid prednicarbat with and without partial wet-wrap dressing in atopic dermatitis.
Dermatology 212(1) , 66-9, (2006) The wet-wrap treatment has been reported to be beneficial in acute episodes of atopic dermatitis (AD) skin lesions.The efficacy of topical corticosteroid prednicarbat with and without additional wet-wrap dressing was investigated in a prospective, randomized ... |
|
|
Transcriptional activity of potent glucocorticoids: relevance of glucocorticoid receptor isoforms and drug metabolites.
Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 16(3) , 143-50, (2003) As compared to standard glucocorticoids (GC), prednicarbate (PC) is favorable in the treatment of eczema due to its high benefit/risk ratio. The remarkable anti-inflammatory effects of PC are in strong contrast to its reported low glucocorticoid receptor (GR)... |
|
|
Steroid-sparing effect of pimecrolimus cream 1% in children with severe atopic dermatitis.
Dermatology 215(4) , 325-30, (2007) To investigate if pimecrolimus cream 1% reduces the need for steroids in the long-term management of severe pediatric atopic dermatitis (AD).A total of 184 pediatric patients (aged 2-17 years) with a history of severe AD according to Rajka and Langeland were ... |
|
|
Modern topical glucocorticoids and anti-infectives for superinfected atopic eczema: do prednicarbate and didecyldimethylammoniumchloride form a rational combination?
Infection 22(6) , 390-4, (1994) The addition of an anti-infective to a topical glucocorticoid preparation for superinfected atopic eczema is still controversial. To address this question in the context of the topical glucocorticoids of the non-halogenated double-ester type 0.25% prednicarba... |
|
|
Atopic dermatitis -- topical therapy: do patients apply much too little?
J. Dermatolog. Treat. 16(2) , 95-101, (2005) The treatment of atopic dermatitis still remains a challenge. Little research has been done on the issue of the extent to which patients correctly use prescribed topical preparations under everyday conditions.To investigate what quantity of topical preparatio... |
|
|
Purpuric generalized lichen nitidus: an unusual eruption simulating pigmented purpuric dermatosis.
Dermatology 208(2) , 167-70, (2004) Generalized haemorrhagic lichen nitidus is rare. To our knowledge, this form of presentation has only been reported once.To describe a new case of generalized haemorrhagic lichen nitidus simulating a pigmented purpuric dermatosis.We document a 24-year-old man... |
|
|
[Mollusca contagiosa in an infant with atopic eczema. A therapeutic challenge].
Hautarzt 55(10) , 991-4, (2004) Molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease frequently observed in children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis, in whom it poses a special therapeutic challenge. A 3-year-old girl presented with atopic eczema and disseminated molluscum contagiosum on her but... |
|
|
Grover's disease associated with pregnancy.
J. Dermatol. 37(4) , 381-3, (2010)
|