Roxarsone
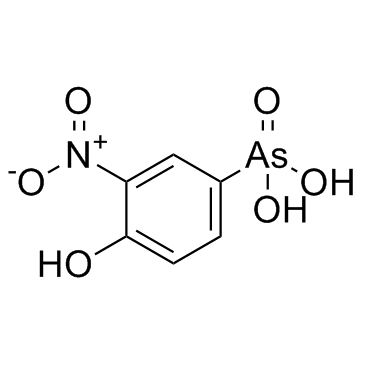
Roxarsone structure
|
Common Name | Roxarsone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 121-19-7 | Molecular Weight | 263.036 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 537.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6AsNO6 | Melting Point | ≥300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 240.3±21.3 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Degradation of roxarsone in a silt loam soil and its toxicity assessment.
Chemosphere 112 , 128-33, (2014) The land application of poultry or swine litter, containing large amounts of roxarsone, causes serious arsenic pollution in soil. Understanding biotransformation process of roxarsone and its potential risks favors proper disposal of roxarsone-contaminated ani... |
|
|
Retention of phenylarsenicals in soils derived from volcanic materials.
J. Hazard. Mater. 186(2-3) , 1328-34, (2011) Sorption of phenylarsenicals including 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylarsonic acid (roxarsone), an animal feed additive widely used for growth stimulation, on soils was investigated in batch systems. Phenylarsonic acid, o-arsanilic acid and roxarsone were retained di... |
|
|
Characterization of Salmonella enterica isolates from turkeys in commercial processing plants for resistance to antibiotics, disinfectants, and a growth promoter.
Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 8(5) , 593-600, (2011) Salmonella enterica isolates from turkeys in two commercial processing plants (1 and 2) were characterized for susceptibility to antibiotics, disinfectants, and the organoarsenical growth promoter, 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylarsonic acid (3-NHPAA, roxarsone), and... |
|
|
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) characterization of trace organoarsenic antimicrobials using silver/polydimethylsiloxane nanocomposites.
Appl. Spectrosc. 65(4) , 423-8, (2011) Organoarsenic drugs such as roxarsone and 4-arsanilic acid are poultry feed additives widely used in US broilers to prevent coccidosis and to enhance growth and pigmentation. Despite their veterinary benefits there has been growing concern about their use bec... |
|
|
Uptake and transport of roxarsone and its metabolites in water spinach as affected by phosphate supply.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 29(4) , 947-51, (2010) Roxarsone (ROX) is widely used as a feed additive in intensive animal production. While an animal is fed with ROX, the As compounds in the manure primarily occur as ROX and its metabolites, including arsenate (As[V]), arsenite (As[III]), monomethylarsonic aci... |
|
|
A proteome investigation of roxarsone degradation by Alkaliphilus oremlandii strain OhILAs.
Metallomics 2(2) , 133-9, (2010) Clostridial species predominate in both chicken gastrointestinal tract as well as litter where the organoarsenical roxarsone (3-nitro 4-hydroxybenzenearsonic acid) is anaerobically transformed releasing the more recognized toxic inorganic arsenic. 2D-gel elec... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of p-arsanilic acid and roxarsone in feed by liquid chromatography-hydride generation online coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry.
J. Environ. Monit. 10(8) , 975-8, (2008) A novel, simple and sensitive liquid chromatography-hydride generation online coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry (LC-HG-AFS) method was developed for simultaneous determination of p-arsanilic acid (p-ASA) and roxarsone in feed. 20% Methanol aqueous... |
|
|
Genome-wide expression analysis of roxarsone-stimulated growth of broiler chickens (Gallus gallus).
Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D. Genomics Proteomics 6(3) , 264-70, (2011) Roxarsone is a commonly used additive in chicken (Gallus gallus) industry. However, little is known on the intrinsic molecular mechanism via which the growth performance of birds improves. This study was therefore performed to investigate the expression profi... |
|
|
In vitro and ex vivo angiogenic effects of roxarsone on rat endothelial cells.
Toxicol. Lett. 223(2) , 175-82, (2013) Roxarsone, a feed additive, is being used worldwide to promote animal growth. However, the potential effect of roxarsone on angiogenesis has not been extensively characterized. We examined the ability of roxarsone to promote angiogenesis of rat endothelial ce... |
|
|
Evaluation of glutathione s-transferase as toxicity indicator for roxarsone and arsanilic acid in Eisenia fetida.
J. Appl. Toxicol. 32(9) , 731-8, (2012) Different compounds can induce stress response by targeting specific genes. Studies related to elucidating the detoxification and adaptive responses of proteins like glutathione-s-transferase (GST) can be helpful in better understanding toxicity. Roxarsone an... |