Monoethylglycinexylidide
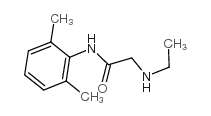
Monoethylglycinexylidide structure
|
Common Name | Monoethylglycinexylidide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7728-40-7 | Molecular Weight | 206.28 | |
| Density | 1.047g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 335.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H18N2O | Melting Point | 242-245ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 127.8ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Transplacental Distribution of Lidocaine and Its Metabolite in Peridural Anesthesia Administered to Patients With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.
Reprod. Sci. 22 , 791-7, (2015) Neonatal effects of drugs administered to mothers before delivery depend on the quantity that crosses the placental barrier, which is determined by the pharmacokinetics of the drug in the mother, fetus, and placenta. Diabetes mellitus can alter the kinetic di... |
|
|
Concentrations of dimethylaniline and other metabolites in milk and tissues of dairy cows treated with lidocaine.
Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 32 , 1256-64, (2015) Lidocaine is a topical anaesthetic drug used in dairy cows for laparotomy (caesarean section, abomasal displacement). Because there are no registered drugs for this indication, it can be applied under the so-called Cascade rules (off-label use), with the rest... |
|
|
MEGX test in hepatology: the long-sought ultimate quantitative liver function test?
J. Hepatol. 19(1) , 4-7, (1993)
|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of lidocaine and its metabolite in peridural anesthesia administered to pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus.
Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 64(12) , 1189-96, (2008) Peridural blockade with lidocaine, bupivacaine, and fentanyl is an anesthetic procedure extensively used in obstetrics, justifying the pharmacokinetic study of these drugs during labor.To investigate the influence of the physiopathological changes of gestatio... |
|
|
Effect of 4% topical lidocaine applied to the face on the serum levels of lidocaine and its metabolite, monoethylglycinexylidide.
Aesthet. Surg. J. 30(6) , 853-8, (2010) Topical lidocaine is a common form of anesthesia for a wealth of procedures across a large number of disciplines, including laser treatments. Preparations can be purchased over the counter with no prescription necessary. It is considered a safer and more acce... |
|
|
Comparison of five commonly-available, lidocaine-containing topical anesthetics and their effect on serum levels of lidocaine and its metabolite monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX).
Aesthet. Surg. J. 32(4) , 495-503, (2012) Topical anesthetics are commonly applied for a variety of indications. Several lidocaine-containing topical anesthetics are available for purchase over the counter (OTC). Recently, the authors' group has shown that there is great interindividual discrepancy i... |
|
|
Efficacy of lidocaine for pain control in subcutaneous infiltration during liposuction.
Aesthet. Surg. J. 29(2) , 122-8, (2009) Liposuction remains the most commonly performed aesthetic surgical procedure in the United States. Preoperative infiltration of the subcutaneous tissues with a wetting solution has become standard. These solutions typically contain some amount of lidocaine fo... |
|
|
Lignocaine plasma levels following topical gel application in laparoscopic and hysteroscopic procedures.
Anaesth. Intensive Care 40(2) , 292-6, (2012) The study aim was to determine plasma lignocaine concentrations resulting from topical application of a newly formulated, sterile two-pack lignocaine gel in laparoscopic and hysteroscopic procedures. This was an open label single-centre study in which six fem... |
|
|
Lidocaine/monoethylglycinexylidide test, galactose elimination test, and sorbitol elimination test for metabolic assessment of liver cell bioreactors.
Artif. Organs 34(6) , 462-72, (2010) Various metabolic tests were compared for the performance characterization of a liver cell bioreactor as a routine function assessment of cultures in a standby for patient application in clinical studies. Everyday quality assessment (QA) is essential to ensur... |
|
|
Reporting a fatality during tumescent liposuction.
Forensic Sci. Int. 178(1) , e11-6, (2008) Deaths of patients during elective surgery have drawn attention to the danger of anesthesia. Tumescent local anesthesia is subcutaneous infiltration of large volumes of dilute lidocaine with epinephrine to produce vasoconstriction while delivering anesthesia ... |