56124-62-0
| Name | Valrubicin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
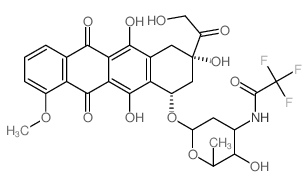
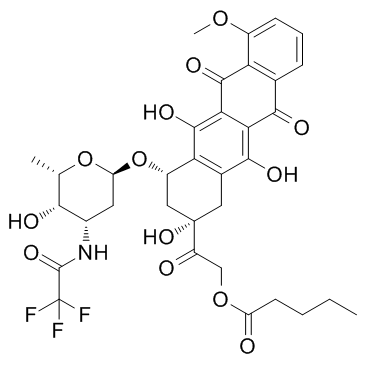
2-Oxo-2-[(2S,4S)-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-({2,3,6-trideoxy-3-[(trifluoroacetyl)amino]-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl}oxy)-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2-tetracenyl]ethyl valerate
Valrubicin 2-oxo-2-[(2S,4S)-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-({2,3,6-trideoxy-3-[(trifluoroacetyl)amino]-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl}oxy)-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-2-yl]ethyl pentanoate Vinorelbine (BICINS ) N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin-14-valerate Pentanoic acid, 2-[(2S,4S)-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-[[2,3,6-trideoxy-3-[(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)amino]-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-2-naphthacenyl]-2-oxoethyl ester trifluoroacetyl-adriamyci14-valerate N-(trifluoroacetyl)adriamycin 14-valerate (AD 32) 2-Oxo-2-[(2S,4S)-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-({2,3,6-trideoxy-3-[(trifluoroacetyl)amino]-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl}oxy)-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-2-yl]ethyl valerate N-Trifluoroacetyldoxorubicin 14-valerate ad32 N-Trifluoroacetyladriamycin 14-valerate Valstar (2S-cis)-Pentanoic Acid 2-(1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-((trifluoroacetyl)amino)-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-2-naphthacenyl)-2-oxoethyl Ester N-trifluoroacetyldoxorubicin-14-valerate antibioticad32 |
| Description | Valrubicin is a chemotherapy agent, inhibits TPA- and PDBu-induced PKC activation with IC50s of 0.85 and 1.25 μM, respectively, and has antitumor and antiinflammatory activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
TPA-activated PKC:0.85 μM (IC50) PDBu-activated PKC:1.25 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Valrubicin (AD 32) is a chemotherapy agent, inhibits TPA- and PDBu-induced PKC activation with IC50s of 0.85 and 1.25 μM, respectively. Valrubicin inhibits the binding of [3H]PDBu to PKC. Therefore, Valrubicin competes with the tumor promoter for the PKC binding site and prevents the latter from both interacting with the phospholipid and binding to PKC[1]. Valrubicin shows cytotoxic activity against squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cell line colony formation, with IC50s and IC90s of 8.24 ± 1.60 μM and 14.81 ± 2.82 μM for UMSCC5 cells, 15.90 ± 0.90 μM, 29.84 ± 0.84 μM for UMSCC5/CDDP‡ cells, and 10.50 ± 2.39 μM, 19.00 ± 3.91 μM for UMSCC10b cells, respectively. Moreover, Valrubicin in combination with radiation enhances the cytotoxicity[2]. |
| In Vivo | Valrubicin (3, 6, or 9 mg) reduces tumor growth at week 3 by intratumoral jection in hamster. Valrubicin (6 mg) combined with minimally cytotoxic irradiation (150, 250, or 350 cGy) causes significant tumor shrinkage in hamster[2]. Valrubicin (0.1 μg/μL) significantly reduces the number of infiltrating neutrophils in biopsies challenged with TPA at 24 h and attenuates chronic inflammation in mice. Valrubicin also decreases the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines in the acute model[3]. |
| Cell Assay | UMSCC5 cells exposed to Valrubicin (2 μM for 3 h), a single dose of radiation (400 cGy), or the combined treatment are cultured for a further 12, 24, or 48 hours. At these times, the cells are collected by trypsinization (0.25%), washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and fixed at 5 × 106 cells/mL with 95% ethanol. Cells are incubated with ribonuclease (50 μg; 70-90 Kunitz units/mg for 30 min), and the resulting pellet resuspended in and incubated with propidium iodide (0.05 mg/mL for 10 min). The DNA content of the samples is determined by flow cytometry according to standard technique[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Hamsters[2] Hamsters with cheek pouch tumors of 100 mm2 are randomly assigned to one of five treatment groups. Momentarily anesthetized animals each receives once a week × 3 injections (27 g × 0.5-inch needle: 0.1 mL administered slowly to the base of the lesion) of Valrubicin (3, 6, or 9 mg) or drug vehicle (Cremophor: alcohol;1:1 by volume; NCl diluent 12). A further group of animals receives anesthesia but no direct tumor treatment (control). Individual tumor sizes are measured with calipers at weekly intervals for 4 weeks, at which time the animals are sacrificed[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 867.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 116-117ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C34H36F3NO13 |
| Molecular Weight | 723.644 |
| Flash Point | 478.6±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 723.213867 |
| PSA | 215.22000 |
| LogP | 6.31 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.619 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~% 
56124-62-0 |
| Literature: RSC Advances, , vol. 3, # 45 p. 22963 - 22966 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |