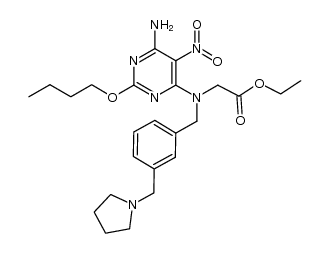
1228585-88-3
| Name | 4-amino-2-butoxy-8-[[3-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)phenyl]methyl]-5,7-dihydropteridin-6-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
6(5H)-Pteridinone, 4-amino-2-butoxy-7,8-dihydro-8-[[3-(1-pyrrolidinylmethyl)phenyl]methyl]-
UNII:O8M467C50G GS 9620 CS-1352 4-amino-2-butoxy-8-(3-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)benzyl)-7,8-dihydropteridin-6(5H)-one UNII-O8M467C50G 4-amino-2-n-butoxy-8-[3'-(pyrrolidin-1"-ylmethyl)-benzyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropteridin-6-one GS-9620 vesatolimod 8-(3-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)benzyl)-4-amino-2-butoxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6(5H)-one 4-Amino-2-butoxy-8-[3-(1-pyrrolidinylmethyl)benzyl]-7,8-dihydro-6(5H)-pteridinone |
| Description | Vesatolimod (GS-9620) is a potent, selective and orally active agonist of Toll-Like Receptor (TLR7) with an EC50 of 291 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC50: 291 nM (TLR7), 9 μM (TLR8)[3] |
| In Vitro | Vesatolimod (GS-9620) rapidly internalizes into cells and preferentially localizes to and signals from endo-lysosomal compartments. To test this hypothesis, the kinetics of cellular uptake of the compound in Daudi cells using tritiated Vesatolimod (3H-GS-9620) is measured. The kinetics of 3H-GS-9620 accumulation is rapid, reaching concentration-dependent steady-state equilibrium in approximately thirty minutes. Measured intracellular concentration of 3H-Vesatolimod is 5-fold higher than the extracellular concentration of 3H-GS-9620 used to treat cells. Increases in intracellular 3H-Vesatolimod concentrations are roughly proportional with increasing concentrations of 3H-GS-9620[1]. |
| In Vivo | Single oral doses of Vesatolimod (GS-9620) at 0.3 and 1 mg/kg in uninfected chimpanzees demonstrates a dose- and exposure-related induction of serum IFN-α, select cytokines/chemokines, and interferon-stimulated genes (ISG) in the peripheral blood and liver. Following oral administration at 0.3 (n=3), and 1 mg/kg (n=3 and n=4), Vesatolimod (GS-9620) Cmax is 3.6±3.5, 36.8±34.5, and 55.4±81.0 nM, respectively. Peak serum interferon responses occur at 8 h post-dose. The mean peak levels of induced serum IFN-α are 66 and 479 pg/mL at doses of 0.3 and 1 mg/kg, respectively. Vesatolimod (GS-9620) treatment induces ISG transcripts including ISG15, OAS-1, MX1, IP-10 (CXCL10), and I-TAC (CXCL11) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) at 0.3 mg/kg and in both PBMC and the liver at 1 mg/kg[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Daudi cells are incubated for indicated times with varying concentrations [3H]Vesatolimod (GS-9620) (0.7μCi/mL). Cell associated radioactivity is extracted with ice cold 80% ethanol and measured using liquid scintillation counting. The total amount of Vesatolimod in cells is calculated from a calibration curve for Vesatolimod (GS-9620) mass versus radioactivity. Cell volume is measured[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Chimpanzee[2] Chimpanzees are used. The trial design includes 4 weeks of pre-study evaluation (Day-28, -13 and just prior to first dose) and two cycles of oral Vesatolimod (GS-9620) treatment every other day three times per week for 4 weeks with one cycle at 1 mg/kg, and, after a one week rest, a second cycle at 2 mg/kg. Animals are also intensely monitored for 14 weeks after treatment to assess tolerability and durability of response. |
| References |
[3]. D Tumas, et al. Preclinical Characterization of GS-9620, A Potent and Selective Oral TLR7 Agonist. |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H30N6O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 410.513 |
| Exact Mass | 410.243011 |
| PSA | 100.10000 |
| LogP | 3.10 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.622 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
|
~% 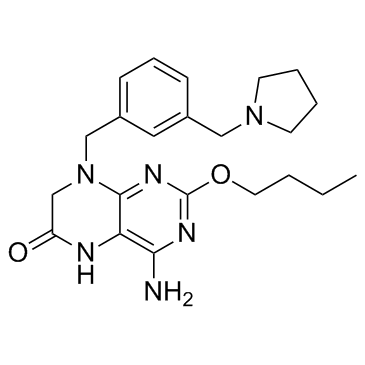
1228585-88-3 |
| Literature: GILEAD SCIENCES, INC.; Delaney, William E.; Link, John O.; Mo, Hongmei; Oldach, David W.; Ray, Adrian S.; Watkins, William J.; Yang, Cheng Yong; Zhong, Weidong Patent: US2013/273005 A1, 2013 ; Location in patent: Paragraph 0363; 0364 ; |
|
~% 
1228585-88-3 |
| Literature: GILEAD SCIENCES, INC.; Delaney, William E.; Link, John O.; Mo, Hongmei; Oldach, David W.; Ray, Adrian S.; Watkins, William J.; Yang, Cheng Yong; Zhong, Weidong Patent: US2013/273005 A1, 2013 ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |