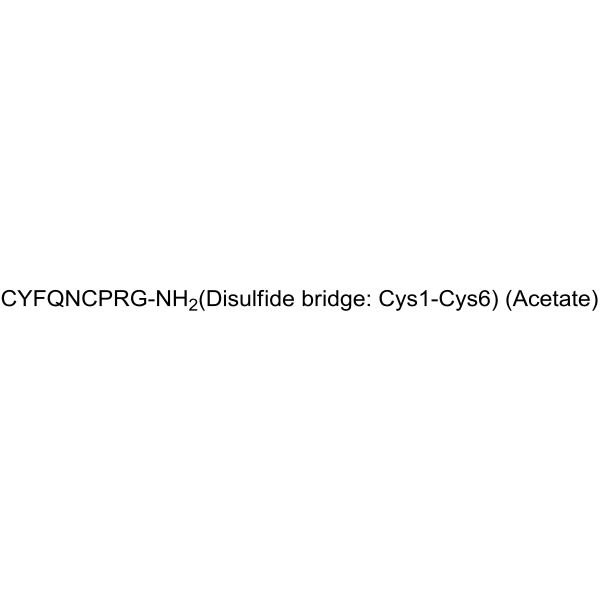75499-44-4
| Name | <8-arginine>vasopressin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Arginine Vasopressin Diacetate |
| Description | Arginine vasopressin (AVP, also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH)) is a 9 amino acid neuropeptide secreted by the posterior pituitary. AVP can regulate the biological effects of fluid balance, osmolality and cardiovascular through three separate G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), namely Avpr1a (V1a), Avpr1b (V1b) and Avpr2 (V2). AVP also have potentially important effects on centrally regulated metabolic processes[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | AVP induces proliferation and prevented cytokine-induced apoptosis in rodent and human beta-cells[1]. Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Line: clonal BRIN BD11 and 1.1B4 cells Concentration: 10-6 M Incubation Time: 2 h Result: Increased proliferation of rodent and human beta-cells. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Line: clonal BRIN BD11 and 1.1B4 cells Concentration: 10-6 M Incubation Time: 2 h Result: Protected against cytokine-induced beta-cell apoptosis. |
| In Vivo | AVP (25 nmol/kg bw; intraperitoneal injection; once) significantly reduces overall AUC glucose values,but not increases insulin levels in mice[1]. Animal Model: NIH Swiss mice (adult; male; 12-14weeks) [1] Dosage: 25 nmol/kg bw Administration: AVP (25 nmol/kg bw; intraperitoneal injection; once) Result: Reduced (P<0.001) overall AUC glucose values,but not increased insulin levels in mice. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C48H69N15O14S2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1144.28000 |
| Exact Mass | 1143.46000 |
| PSA | 549.33000 |
| LogP | 1.25190 |