1050-28-8
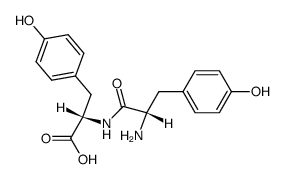
| Name | L-tyrosyl-L-tyrosine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | h-tyr-tyr-oh |
| Description | H-Tyr-Tyr-OH (L-Tyrosyl-L-tyrosine) is an antihypertensive peptide. H-Tyr-Tyr-OH inhibits angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) with an IC50 value of 0.028 mg/mL. H-Tyr-Tyr-OH can be used for the research of high blood pressure[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.028 mg/mL (ACE)[2] |
| In Vitro | H-Tyr-Tyr-OH shows inhibitory effect against ACE with an IC50 value of 0.028 mg/mL[2]. |
| In Vivo | H-Tyr-Tyr-OH (12.5 mg/kg; intraarterial injection once) effects systolic blood pressure in vivo[1]. H-Tyr-Tyr-OH (0-100 mg/kg; i.p. once) effects blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats[1]. Animal Model: Anesthetized male SpragueDawley rats[1] Dosage: 12.5 mg/kg Administration: Intraarterial injection; 12.5 mg/kg once Result: Significantly elevated systolic blood pressure, with a peak increase of 5 min after administration. Animal Model: Spontaneously hypertensive rats[1] Dosage: 0, 50 and 100 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; once Result: Significantly reduced blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats, even at a dose of 50 mg/kg. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C18H20N2O5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 344.36200 |
| Exact Mass | 344.13700 |
| PSA | 132.88000 |
| LogP | 1.87090 |
| Vapour Pressure | 9.55E-21mmHg at 25°C |
|
~% 
1050-28-8 |
| Literature: Abderhalden et al. Fermentforschung, 1942 , vol. 16, p. 98,114 Bergmann et al. Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift fuer Physiologische Chemie, 1934 , vol. 224, p. 17,24 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |