537049-40-4
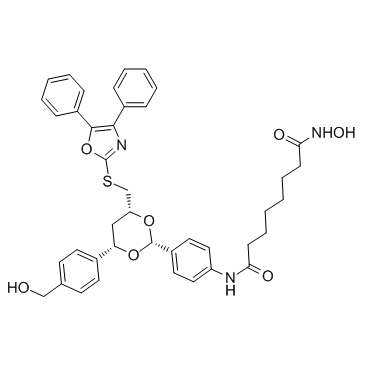
| Name | Octanediamide, N1-[4-[(2R,4R,6S)-4-[[(4,5-diphenyl-2-oxazolyl)thio]methyl]-6-[4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-1,3-dioxan-2-yl]phenyl]-N8-hydroxy-, rel |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII:02C2G1D30D
N-(4-{(2R,4R,6S)-4-{[(4,5-Diphenyl-1,3-oxazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-6-[4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-1,3-dioxan-2-yl}phenyl)-N'-hydroxyoctanediamide |
| Description | Tubacin is a potent and selective inhibitor of HDAC6, with an IC50 value of 4 nM and approximately 350-fold selectivity over HDAC1. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HDAC6:4 nM (IC50) HDAC3:1.27 μM (IC50) HDAC8:1.27 μM (IC50) HDAC1:1.40 μM (IC50) HDAC5:3.35 μM (IC50) HDAC10:3.71 μM (IC50) HDAC11:3.79 μM (IC50) HDAC9:4.31 μM (IC50) HDAC2:6.27 μM (IC50) HDAC7:9.70 μM (IC50) HDAC4:17.30 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Tubacin preferentially induces α-tubulin hyperacetylation at a concentration of 2.5 µM, and induces α-tubulin acetylation at 5 µM and protects prostate cancer (LNCaP) cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced death at 8 µM via peroxiredoxin acetylation[1]. Tubacin (2.5 and 5 μM) specifically induces acetylation of α-tubulin in MM cells. Tubacin significantly inhibits both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant MM cell growth, with IC50 5-20 μM at 72 h. Tubacin also induces apoptosis by activation of caspases. Moreover, Tubacin inhibits binding of HDAC6 with dynein, and it induces significant accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins, when combined with bortezomib. Tubacin and bortezomib induce synergistic antitumor activity in MM cell lines, and inhibits paracrine MM Cell Growth. Tubacin (5 μM) synergistically enhances bortezomib-induced cytotoxicity in patient MM cells without cytotoxicity to PBMCs[2]. Tubacin can concentration-dependently inhibits JEV-induced cytopathic effect and apoptosis, as well as reduces virus yield in human cerebellar medulloblastoma cells. The IC50 of virus yield is 0.26 μM for Tubacin. Tubacin also meaningfully blocks the production of intracellular infectious virus particles, with an IC50 of 1.52 μM. Tubacin induces the hyperacetylation of a HDAC6 substrate Hsp90 and reduces the interaction of Hsp90 with JEV NS5 protein[3]. |
| Cell Assay | HDAC inhibitors TSA, VPA, tubacin, and TBSA are used in the assay. Cytotoxicity of HDACi to TE671 and BHK-21 cells is evaluated by MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay. 5 × 104 cells per well are seeded in 96-well plates and then treated with the indicated concentration of each HDACi. After 48-h of treatment, 25 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL) is added to each well and incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for 3 h. After three washings with phosphate buffer saline (PBS), 100 μL DMSO is added into each well for dissolving formazan crystals. OD570−630 is measured by micro-ELISA reader and survival rate are calculated to indicate suppressive effects of each HDACi on the survival of TE671 and BHK-21 cells. Survival rate (%) = ((Acontrol − Aexperiment)/Acontrol) × 100%. 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC50) values are calculated by computer program[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C41H43N3O7S |
| Molecular Weight | 721.861 |
| Exact Mass | 721.282166 |
| PSA | 168.45000 |
| LogP | 5.82 |
| Appearance | white to tan |
| Index of Refraction | 1.668 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: ≥10mg/mL |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|