320725-47-1
| Name | 1-(Diphenylmethyl)hydrazine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
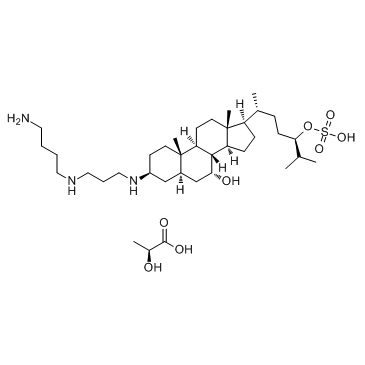
(2S)-2-Hydroxypropanoic acid - (3β,5α,7α,24R)-3-({3-[(4-aminobutyl)amino]propyl}amino)-7-hydroxycholestan-24-yl hydrogen sulfate hydrate (1:1:1)
squalamine lactate |
| Description | Squalamine lactate is an aminosterol compound discovered in the tissues of the dogfish shark, with antimicrobial activity, and used for the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Squalamine lactate has a more generalized effect on the cellular signaling cascade that is common to both VEGF and other growth factors[1]. Squalamine blocks the action of VEGF and integrin expression, thereby inhibiting angiogenesis, when bound to calmodulin[2]. |
| In Vivo | Squalamine is ineffective when administered intravitreally and therefore requires intravenous dosing. However, systemic dosing has yielded promising results in rats as well as humans[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C37H71N3O8S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 736.055 |
| Exact Mass | 735.506775 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |