199796-52-6
| Name | DHA-paclitaxel |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PACLITAXEL DOCOSAHEXAENOIC ACID
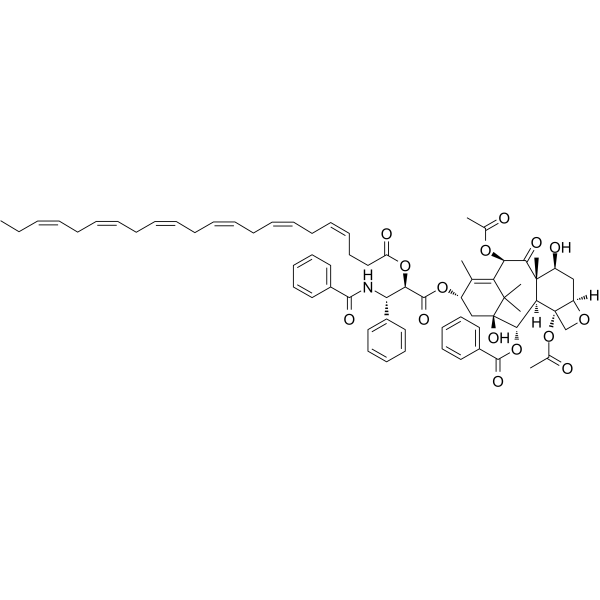
UNII-OJE5810C4F Taxoprexin Benzenepropanoic acid, β-(benzoylamino)-α-[[(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-1-oxo-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaen-1-yl]oxy]-, (2aR,4S,4aS,6R,9S,11S,12S,12aR,12bS)-6,12b-bis(acetyloxy)-12-(benzoyloxy)-2a,3 ,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4,11-dihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-7,11-methano-1H-cyclodeca[3,4]benz[1,2-b]oxet-9-yl ester, (αR,βS)- DHA-paclitaxel (2α,5β,7β,10β,13α)-4,10-Diacetoxy-13-({(2R,3S)-3-(benzoylamino)-2-[(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoyloxy]-3-phenylpropanoyl}oxy)-1,7-dihydroxy-9-oxo-5,20-epoxytax 
-11-en-2-yl benzoate |
| Description | DHA-paclitaxel is an inert prodrug composed of the natural fatty acid DHA covalently linked to the C2'-position of paclitaxel. The paclitaxel moiety binds to tubulin and inhibits the disassembly of microtubules, thereby resulting in the inhibition of cell division. Compared to Paclitaxel, DHA-Paclitaxel targets tumor cells more specifically because tumor cells absorb large amounts of natural fatty acids for use as biochemical precursors and energy sources. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C69H81NO15 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1164.38 |