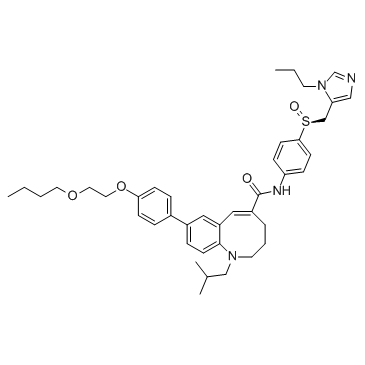
497223-25-3
| Name | Cenicriviroc |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cenicriviroc
(5E)-8-[4-(2-Butoxyethoxy)phenyl]-1-isobutyl-N-(4-{(S)-[(1-propyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]sulfinyl}phenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-benzazocine-5-carboxamide MFCD28502076 1-Benzazocine-5-carboxamide, 8-[4-(2-butoxyethoxy)phenyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-(2-methylpropyl)-N-[4-[(S)-[(1S)-(1-propyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]sulfinyl]phenyl]-, (5E)- |
| Description | Cenicriviroc is an orally active, dual CCR2/CCR5 antagonist, also inhibits both HIV-1 and HIV-2, and displays potent anti-inflammatory and antiinfective activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CCR5:0.29 nM (IC50) CCR2:5.9 nM (IC50) R5 HIV-1:0.024-0.08 nM (IC50, in PBMCs) R5 HIV-2:0.03-0.98 nM (IC50, in PBMCs) |
| In Vitro | Cenicriviroc prevents human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) from cellular entry[2]. Regarding the 4 R5 HIV-2 clinical isolates tested, effective concentration 50% EC50 for cenicriviroc are 0.03, 0.33, 0.45 and 0.98 nM. The dual-tropic and the X4-tropic HIV-2 strains are resistant to cenicriviroc with EC50 at >1000 nM, and MPI at 33% and 4%, respectively[3]. |
| In Vivo | Cenicriviroc (≥20 mg/kg/day) significantly reduces monocyte/macrophage recruitment in vivo. At these doses, cenicriviroc shows antifibrotic effects, with significant reductions in collagen deposition, and collagen type 1 protein and mRNA expression across the three animal models of fibrosis. In the NASH model, cenicriviroc significantly reduces the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease activity score. Cenicriviroc treatment has no notable effect on body or liver/kidney weight[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Male C57BL/6 mice (n=44; 8-10 weeks of age) are allocated to receive treatments via oral gavage (PO) on Days 1-5 in the following groups: non-disease control, vehicle control twice daily (BID), Cenicriviroc 5 mg/kg/day (Cenicriviroc5) BID, Cenicriviroc 20 mg/kg/day (Cenicriviroc20) BID, Cenicriviroc 100 mg/kg/day (Cenicriviroc100) BID, Cenicriviroc20 QD, and positive control dexamethasone (corticosteroid known to reduce inflammation in a variety of animal models) 1 mg/kg QD. On Day 4, peritonitis is induced via IP injection of TG 3.85% (1 mL/animal) 2 hours post-dose in all groups except non-disease controls. Study endpoints includes: peritoneal lavage cell counts and pharmacokinetic (PK) evaluation. Animals are sacrificed 48 hours post-TG injection by isoflurane inhalation, and peritoneal lavage and blood samples (0.7 mL) are collected. Differential cell counts are assessed in peritoneal lavage samples with multispecies software and an analysis software designed for mouse peritoneal fluid on. A 0.3 mL aliquot of the blood sample is processed to plasma for PK analysis. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 913.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C41H52N4O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 696.941 |
| Flash Point | 506.3±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 696.370911 |
| LogP | 10.22 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.603 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |