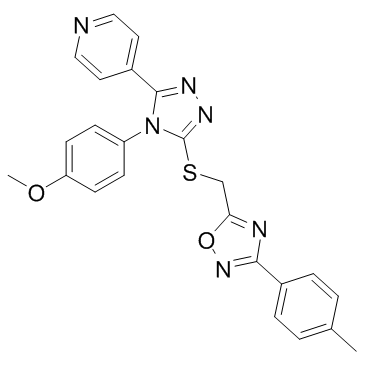
| Description |
JW74 antagonizes LiCl-induced activation of the canonical Wnt signaling with an IC50 of 420 nM.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
IC50: 420 nM (Wnt)[1]
|
| In Vitro |
JW74 shows a reduction of canonical Wnt signaling in the ST-Luc assay with an IC50 of 790 nM[1]. The effect of tankyrase inhibition on cellular viability is tested by performing an MTS assay. The cellular viability of U2OS cells treated for 72 h treatment with 10 μM JW74 is reduced to 80%, relative to DMSO-treated cells. Flow cytometry is also performed to determine the expression marker Ki-67 in U2OS following 48 h treatment with DMSO or 10 uM JW74. Ki-67 expression is reduced from 97.5% in DMSO-treated cells to 86.7% in JW74-treated cells[2].
|
| In Vivo |
The in vivo efficacy of JW74 is tested using SW480 cell xenografts. A relatively high dose of JW74 (150 or 300 mg/kg) is used because of a rapid compound degradation in the organism as indicated in the human liver microsome analysis (t1/2=2.5 minutes) and in pharmacokinetic analyses (after per oral injections: t1/2=30 minutes and intravenous injections: t1/2=15 minutes). The presence of JW74 in tumors and plasma is identified by mass spectrometry. JW74 concentration in tumors is in the range 4.2 to 72.1 μmol/kg for JW74 150 mg/kg, 1.9 to 11.1 μmol/kg for JW74 300 mg/kg, and 2.8 μM in plasma for both doses[1].
|
| Cell Assay |
The cell lines U2OS, SaOS-2, and KPD are cultured in RPMI-1640. Two to three thousand cells attached overnight in 96-well plates are treated with culturing medium containing 0.1% DMSO (control) or JW74 (10-0.1 μM). Proliferation rates based on cell confluence are determined by live cell imaging. Cellular viability is also determined by MTS assay. Expression of the proliferation marker Ki-67 is performed by staining cells with PE-mouse anti-human Ki-67 and by analyzing the expression by flow cytometry[2].
|
| Animal Admin |
Mice[1] 40 female C.B-Igh-1b/IcrTac-Prkdcscid mice are injected subcutaneously (s.c.) at the right posterior flank with 107 SW480 cells diluted in 100 μL PBS. Injections are initiated when tumor formation is visible in 50 % of the animals (7 days). Mice are randomized and divided into three treatment groups: JW74 150 mg/kg, JW74 300 mg/kg and vehicle control, 1 % Tween 80. Daily intra peritoneal (i.p.) injections (200 μL) with two day injection intermissions after every fifth injection day are performed until the experiment end (29 days). At the termination day, 24 hours after the last injection, blood is collected after cardiac puncture and tumors are dissected and weighed. The compound concentration in tumors and blood are determined using on-line and off-line Solid Phase Extraction-Capillary Liquid Chromatography (SPE-CapLC) instrumentation coupled to a Time of Flight (TOF) mass spectrometer. A Zorbax SB C18 5 μm 150×0.3 mm column is used for separation, and a Knauer K-2600 UV detector is used as a complimentary detector.
|
| References |
[1]. Waaler J, et al. Novel synthetic antagonists of canonical Wnt signaling inhibit colorectal cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2011 Jan 1;71(1):197-205. [2]. Stratford EW, et al. The tankyrase-specific inhibitor JW74 affects cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis and differentiation in osteosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Med. 2014 Feb;3(1):36-46.
|