936694-12-1
| Name | Glesatinib |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII:7Q29OXD98N
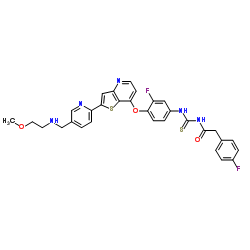
7Q29OXD98N N-[(3-Fluoro-4-{[2-(5-{[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]methyl}-2-pyridinyl)thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-yl]oxy}phenyl)carbamothioyl]-2-(4-fluorophenyl)acetamide Benzeneacetamide, 4-fluoro-N-[[[3-fluoro-4-[[2-[5-[[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]methyl]-2-pyridinyl]thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-yl]oxy]phenyl]amino]thioxomethyl]- Glesatinib |
| Description | Glesatinib (MGCD265) is an orally active, potent MET/SMO dual inhibitor. Glesatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, antagonizes P-glycoprotein (P-gp) mediated multidrug resistance (MDR) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
MET |
| In Vitro | Glesatinib (MGCD265; 0.01-5 μM; for 72 hours) results in a dose-dependent inhibition of cancer cell growth and shows the low IC50 value of 0.08 μM on NSCLC H1299 cells[1]. Glesatinib (0.01, 0.1, 0.5, 1 μM) significantly increases by several-fold the percentage of apoptotic cells in NSCLC H1299 cells[1]. Glesatinib has the cytotoxicity to P-gp overexpressing cancer cells KB-C2, SW620/Ad300, HEK293/ABCB1, and their parent cells KB-3-1, SW620, HEK293 cells with the IC50s fell between 5 and 10 μM[1]. Glesatinib (1, 3 μM; 120 mins) increases the intracellular [3H]-Paclitaxel accumulation and inhibits [3H]-Paclitaxel efflux in cancer cell lines overexpressing P-gp[2]. Glesatinib (0-40 μM) stimulates the ATPase activity of P-gp transporters in a dose-dependent manner[2]. Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Line: NSCLC H1299 cells Concentration: 0.01, 0.1, 1, 2, 5 μM Incubation Time: For 72 hours Result: Resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of cancer cell growth and showed the lowest IC50 value of 0.08 μM. |
| In Vivo | Glesatinib (MGCD265; 15 mg/kg/day; orally; 40 weeks) causes a significant decrease in tumor size[1]. Animal Model: 4−6-week old female balb/c athymic (nu/nu) mice with HCC827 NSCLC tumor xenografts[1] Dosage: 15 mg/kg Administration: Orally; daily; 40 weeks Result: Caused a significant decrease in tumor size. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C31H27F2N5O3S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 619.705 |
| Exact Mass | 619.152344 |
| LogP | 6.50 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.672 |