552-98-7
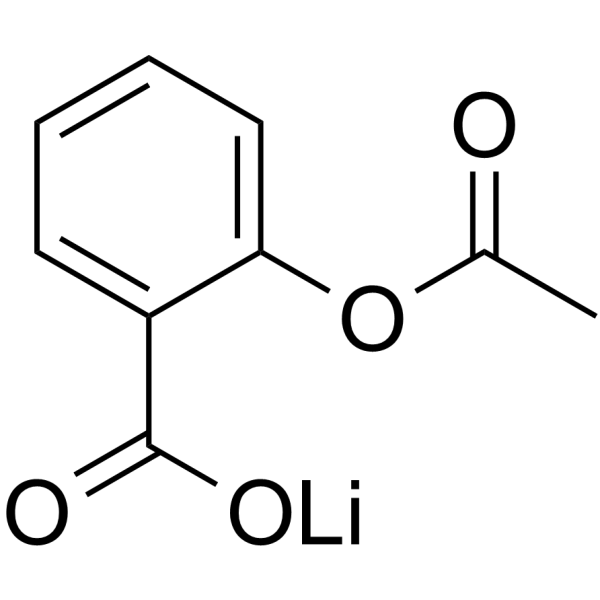
| Name | lithium,2-acetyloxybenzoate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
lithium 2-acetoxybenzoate
EINECS 209-029-5 lithium O-acetylsalicylate Lithium acetylsalicylate 2-acetoxy-benzoic acid,lithium-salt 2-Acetoxy-benzoesaeure,Lithium-Verbindung 2-Acetoxy-benzoesaeure,Lithium-Salz |
| Description | Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid) lithium is an orally active, potent and irreversible inhibitor of cyclooxygenase COX-1 and COX-2, with IC50 values of 5 and 210 μg/mL, respectively. Aspirin lithium induces apoptosis. Aspirin lithium inhibits the activation of NF-κB. Aspirin lithium also inhibits platelet prostaglandin synthetase, and can prevent coronary artery and cerebrovascular thrombosis[1][2][3][4][5][6]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-1 COX-2 |
| In Vitro | Aspirin lithium inhibits COX-1 and COX-2 in human articular chondrocytes, with IC50 values of 3.57 μM and 29.3 μM, respectively[2]. Aspirin lithium acetylates serine-530 of COX-1, thereby blocking thromboxane A synthesis in platelets and reducing platelet aggregation[3]. Aspirin lithium inhibits COX-2 protein expression through interference with binding of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta) to its cognate site on COX-2 promoter/enhancer[3]. Aspirin lithium inhibits NF-κB-dependent transcription from the lgκ enhancer and the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) long terminal repeat (LTR) in transfected T cells[4]. Aspirin lithium induces apoptosis by the activation of caspases, the activation of p38 MAP kinase, release of mitochondrial cytochrome c, and activation of the ceramide pathway[6]. |
| In Vivo | Aspirin lithium (5-150 mg/kg, PO, once) shows significant antipyretic activity in adult yeast-fevered male rats[7]. Animal Model: Male albino Charles River rats (200-250 g, 8 animals/group, fever was induced by 20 ml/kg of a 20 % aqueous suspension of brewer’s yeast which was injected SC in the back below the nape of the neck)[7] Dosage: 5, 25, 50, 100 and 150 mg/kg Administration: PO, once Result: Produced a statistically significant decrease of 0.23 ℃ at 15 min post-drug at the dose of 150 mg/kg. Antipyretic effect gradually increased in magnitude until a peak effect of 1.96 ℃ was reached at 120 min post-drug. The ED50 of aspirin was found to be 10.3 mg/kg with confidence limits of 1.8-23.0 mg/kg. The antipyretic response to aspirin is dependent on the dose of the compound administered. |
| References |
[6]. Elwood PC, et al. Aspirin, salicylates, and cancer. Lancet. 2009 Apr 11;373(9671):1301-9. |
| Boiling Point | 321.4ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H7LiO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 186.09000 |
| Flash Point | 131.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 186.05000 |
| PSA | 66.43000 |
| HS Code | 2918229000 |
|---|
|
~% 
552-98-7 |
| Literature: Gerngross; Kersasp Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1914 , vol. 406, p. 252 |
| HS Code | 2918229000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918229000. other o-acetylsalicylic acid salts and esters. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:9.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
