60786-59-6
| Name | G Oxytocin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3,3-DiallylthiacarbocyanineBromide
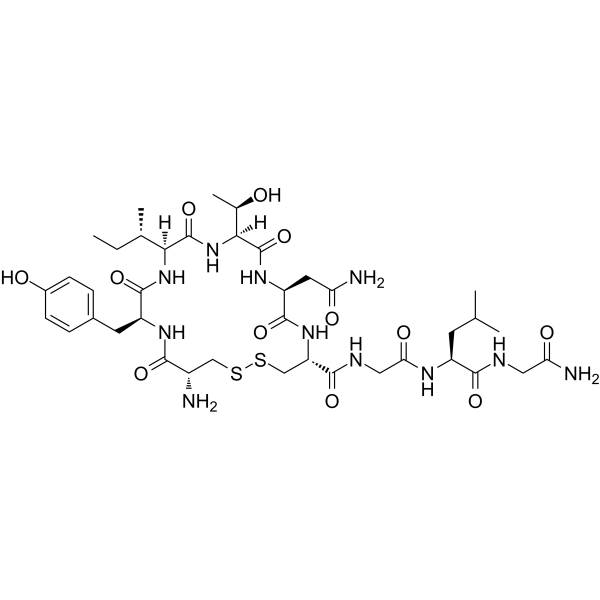
CYS-TYR-ILE-THR-ASN-CYS-GLY-LEU-GLY-NH2 [THR4,GLY7] OT H-CYS-TYR-ILE-THR-ASN-CYS-GLY-LEU-GLY-NH2,(DISULFIDE BOND) Cys-Tyr-Ile-Thr-Asn-Cys-Gly-Leu-Gly-NH2 (Disulfide bridge Cys1-Cys6) TGOT H-CYS-TYR-ILE-THR-ASN-CYS-GLY-LEU-GLY-NH2 thr(4)-gly(7)-oxytoci [THR4,GLY7]-OXYTOCIN |
| Description | (Thr4,Gly7)-Oxytocin, an Oxytocin analogue, is a specific OT receptor agonist. (Thr4,Gly7)-Oxytocin also excites subicular neurons via activation of TRPV1 channels, and depression of K+ channels. [1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
OT receptors, K+ channels[1]. |
| In Vitro | (Thr4,Gly7)-Oxytocin (1 μM, 1 min) evokes an inward current of 5.9 pA in paraventricular thalamus (PVT) neurons[1]. (Thr4,Gly7)-Oxytocin (1 μM, 1 min) increases spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) frequency in PVT neurons[1]. (Thr4,Gly7)-Oxytocin (0.3 μM, 5 min) induces depolarization in both bursting cells and regular firing cells[2]. (Thr4,Gly7)-Oxytocin (0.3 μM, 5 min) depolarizes subicular neurons by activating TRPV1 channels[2]. |
| In Vivo | (Thr4,Gly7)-Oxytocin (1 μM, direct intra-PVT infusion for 1 min) evokes depolarization on TGOT-responsive neurons in mice[1]. (Thr4,Gly7)-Oxytocin (100 ng, intracerebroventrical injection) increases nitric oxide production in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male rats[3]. Animal Model: Swiss Webster mice [1] Dosage: 1 μM Administration: Intratracheal administration for 24 h Result: Excited 34.3% of aPVT neurons, 57.6% of mPVT neurons, and 60.0% of pPVT neurons. Increased the firing rate of TGOT-responsive PVT neurons in all subregions. |
| References |
| Density | 1.332g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C39H61N11O12S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 940.09800 |
| Exact Mass | 939.39400 |
| PSA | 436.06000 |
| LogP | 0.54950 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.587 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 20 |
| Safety Phrases | 36/37/39-45 |