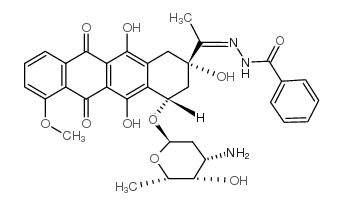
54083-22-6
| Name | N-[(E)-1-[(2S,4S)-4-(4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-tetracen-2-yl]ethylideneamino]benzamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Rubidazone
ZORUBICIN Zorubicina [INN-Spanish] zorubicine Benzoylhydrazone daunorubicin Zorubicin [INN] daunomycin benzoylhydrazone Zorubicine [INN-French] Rubidazon Zorubicinum [INN-Latin] |
| Description | Zorubicin (Rubidazon) is a derivative of Daunorubicin (HY-13062A). Zorubicin interacts with topoisomerase II and inhibits DNA polymerases. Zorubicin can be used for the research of acute leukemias and sarcomas[1][2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Zorubicin (0.1-1 μg/mL; 0-24 h) affects cell cycle[2]. Zorubicin (0-128 nM/mL; 20 min) dose-dependently inhibits DNA polymerases α and β, and shows preferential inhibition of polymerase α[3]. Cell Cycle Analysis[2]. Cell Line: Human lymphoid cell line Concentration: 0.1-1 μg/mL Incubation Time: 0-24 hours Result: Time-dependently increased G2-accumulations of human lymphoid cells, delayed the traverse through G1 and the G1-S transition. Caused a stepwise accumulation of cells in G2-phase. |
| In Vivo | Zorubicin (12-18 mg/kg; i.p. 48 h after tumour cells injection) affects leukaemic colony forming units[1]. Zorubicin (0.75-6.0 mg/kg; i.v.) increases plasma histamine concentrations and produces immediate hypotension in anesthetized beagle dogs[3]. Animal Model: Six- to eight-week-old male DBA2 mice with P388 tumour cells[1] Dosage: 12-18 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection ; 12-18 mg/kg; 48 h after tumour cells injection Result: Showed a D1/2 value of 1.6 mg/kg for leukaemic colony forming units. |
| Density | 1.54g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C34H35N3O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 645.65600 |
| Exact Mass | 645.23200 |
| PSA | 210.23000 |
| LogP | 3.33700 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|