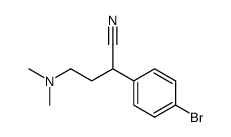
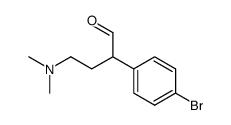
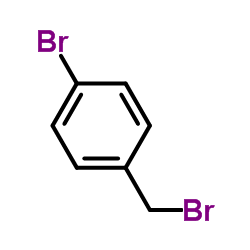
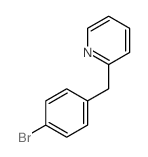
86-22-6
| Name | brompheniramine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Brompheniramine
MFCD00865691 EINECS 201-657-8 (+/-)-1-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(2-pyridyl)-3-dimethylaminopropane (±)-brompheniramine |
| Description | Brompheniramine ((±)-Brompheniramine) is a potent and orally active antihistamine of the alkylamine class. Brompheniramine is a selective histamine H1 receptor antagonist with a Kd of 6.06 nM. Brompheniramine can block the hERG channels, calcium channels, and sodium channels with IC50s of 0.90 μM, 16.12 μM and 21.26 μM, respectively. Brompheniramine has anticholinergic, antidepressant and anesthetic properties and can be used for allergic rhinitis research[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Brompheniramine (0.1-100 μM) blocks hERG K+ channels expressed in CHO cells in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 0.90±0.14 μM, and reduced peak tail current amplitude measured at -60 mV (cells are depolarized for 2 s to +20 mV from a holding potential of -80 mV followed by a 3s repolarization back to -60 mV)[3]. Brompheniramine (1, 10 and 100 μM) significantly shortens the APD50 and depresses the plateau phase on the action potential in guinea pig papillary muscle, as well as slightly prolongs the APD90 in guinea pig papillary muscle at 10 and 100 μM[3]. Brompheniramine (0.1-100 μM) inhibit the amplitude of the Ca2+ channel currents in rat ventricular myocytes by 14.1±1.1, 31.1±5.8, 38.0±3.8 and 90.2±3.7% at 0.1, 1, 10 and 100 μM, respectively[3]. Brompheniramine blocks muscarinic cholinergic receptors in human chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells[4]. |
| In Vivo | Brompheniramine (0.3-3 μM; SC, single dosage) induces cutaneous analgesia in rats[1]. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats[1] Dosage: 0.3, 0.6, 1.1, 1.5 and 3.0 μM Administration: SC, single dosage Result: Provoked cutaneous analgesia in a dose-dependent manner, with an EC50 value of 0.66 μM, and induced prolonged analgesic duration. |
| References |
| Density | 1.265 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 403ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19BrN2 |
| Molecular Weight | 319.23900 |
| Flash Point | 197.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 318.07300 |
| PSA | 16.13000 |
| LogP | 3.92770 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.577 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
|
~68% 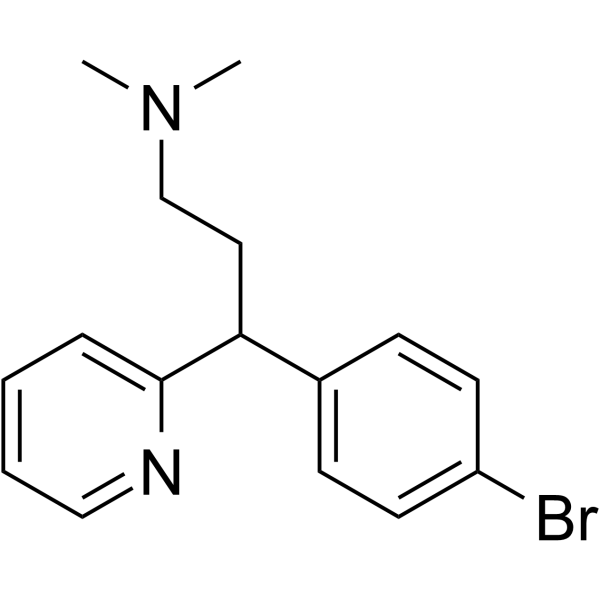
86-22-6 |
| Literature: Botteghi, Carlo; Chelucci, Giorgio; Ponte, Gino Del; Marchetti, Mauro; Paganelli, Stefano Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1994 , vol. 59, # 23 p. 7125 - 7127 |
|
~% 
86-22-6 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 59, # 23 p. 7125 - 7127 |
|
~% 
86-22-6 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 59, # 23 p. 7125 - 7127 |
|
~% 
86-22-6 |
| Literature: Yakugaku Zasshi, , vol. 72, p. 1529 Chem.Abstr., , p. 8080 |
|
~% 
86-22-6 |
| Literature: Yakugaku Zasshi, , vol. 72, p. 1529 Chem.Abstr., , p. 8080 |
|
~% 
86-22-6 |
| Literature: Yakugaku Zasshi, , vol. 72, p. 1529 Chem.Abstr., , p. 8080 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |