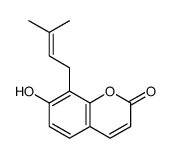
484-12-8
| Name | osthol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ostol
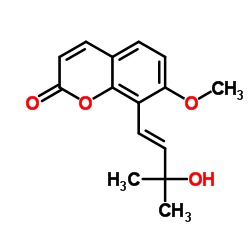
7-methoxy-8-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one MFCD00076049 Cnidium Monnieri Extract DaMiana Extract 7-methoxy-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chromen-2-one 7-Methoxy-8-isopentenylcoumarin 7-Methoxy-8-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)coumarin Osthol/Osthole 7-Methoxy-8-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one 7-methoxy-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-2H-chromen-2-one 7-methoxy-8-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one Ostole 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 7-methoxy-8-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)- 7-methoxy-8-isopentenoxycoumarin 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 7-methoxy-8- (3-methyl-2-butenyl)- 7-Methoxy-8-(3-Methyl-But-2-Enyl)-Chromen-2-One Chuanxiongzine Osthole 7-methoxy-8-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one Coumarin, 7-methoxy-8- (3-methyl-2-butenyl)- OSTHOL Cnidium 7-Methoxy-8-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)coumarin,7-Methoxy-8-isopentenylcoumarin,Osthol 7-Méthoxy-8-(3-méthyl-2-butèn-1-yl)-2H-chromén-2-one |
| Description | Osthole is a natural antihistamine alternative. Osthole may be a potential inhibitor of histamine H1 receptor activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Histamine H1 receptor[1] |
| In Vitro | Osthole (p<0.0001) and Fexofenadine (p<0.001) inhibit increased HRH-1 mRNA expression induced by histamine in the study group. This result is also observed in cells cultured with histamine/Osthole; where combined substances decreased HRH-1 mRNA expression compared to histamine (p<0.0001)[1]. Assessment of cell viability does not detect obvious toxicity when Osthole is used at a dose up to 100 µM. However, when the dose reached 500 µM, Osthole started to show toxic effect. Based on these observations, Osthole is used in all in vitro studies at the dose range of 10 to 100 µM. Osthole dose-dependently promotes osteoblast differentiation, as shown by the upregulation of osteoblast differentiation marker genes such as type I collagen (col1), bone sialoprotein (BSP) and osteocalcin (OC) (2 days of culture). Osthole promotes ALP activity in mouse primary osteoblasts in a dose-dependent manner[2]. |
| In Vivo | Subcutaneous injection of Osthole at a dose of 5 mg/kg per day onto mouse calvariae significantly stimulates local bone formation, as shown by histologic analysis of calvarial samples harvested 2 weeks after the last injection and stained with H&E orange G. Histomorphometric analysis reveals that Osthole has a significant effect on bone formation as potent as the positive control, the microtubule inhibitor TN-16. This effect, however, is not seen when Osthole is used at a dose of 1 mg/kg per day. Intraperitoneal injection of Osthole for 8 weeks significantly reverses bone loss in the ovariectomized rats. Histologic examination of the L4samples stained with trinitrophenol poinsettia demonstrates a partial recovery of the trabecular structure in ovariectomized rats treated with Osthole. Histomorphometric analysis shows that treatment with Osthole significantly increases total BMD, trabecular bone volume, and trabecular thickness and decreases trabecular separation[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Peripheral blood samples are collected from participants between 7.00 and 9.00 a.m. on the first study day and these are concentrated in grouping tubes with K3EDTA. Fresh PBMCs are then prepared. Isolated cells are seeded on 24-well plates at 1×106 per well with RPMI-1640 and supplemented with 1% heat inactivated human AB serum, 1% gentamicin and 0.25% PHA. Active reagents are added to each well after 24 h and pure medium formed the control for each substance. Cells are then harvested after a further three days[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Four-week-old ICR Swiss mice are injected subcutaneously over the calvarial surface with or without the treatment of Osthole twice a day for 5 consecutive days at the doses of 1 and 5 mg/kg per day (3 mice per group). Microtubule inhibitor TN-16 is used as a positive control (5 mg/kg per day, by subcutaneous injection, twice a day for 2 days; 3 mice per group). All mice are euthanized 3 weeks after treatment, and calvariae are dissected, fixed in 10% phosphate-buffered formalin for 2 days, decalcified in 10% EDTA for 2 weeks, and embedded in paraffin. Histologic sections are cut and stained with hematoxylin and eosine orange G. New bone area over the calvarial surface is quantified by histomorphometry using the OsteoMeasure System. To measure mineral appositional rate (MAR) and bone-formation rate (BFR), double calcein labeling is performed at days 7 and 14 by intraperitoneal injection (20 mg/kg), and mice are euthanized 7 days after the second labeling. The labeling is examined in plastic sections. The dissected calvarial samples are fixed in 75% ethanol and embedded in methyl methacrylate. Unstained transverse sections (3 µm thick) are examined with a fluorescent microscope. MAR and BFR are measured using the OsteoMeasure System. Rats[2] Thirty 6-month-old female Sprague-Dawley rats are used. After anesthesia with intraperitoneal nembutal injection (30 mg/kg), the rats are randomized by body weight into three groups for the surgery (n=10/group): group 1: sham surgery followed by PBS vehicle treatment (sham+VEH); group 2: ovariectomy followed by vehicle treatment (OVX+VEH); and group 3: ovariectomy followed by Osthole treatment (OVX+OST). The treatment is started 1 month after surgery and continued for 8 weeks. Vehicle or Osthole (100 mg/kg per day) is administered orally once a day for 8 weeks. Before rats are euthanized at the end of the experiments, the total bone mineral density (BMD, g/m2) is measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. The fourth lumbar vertebrae (L4) then are dissected for histomorphometric and micro-computed tomographic (µCT) analysis, and the left femoral shafts are used for biomechanical testing. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 396.7±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 83-84°C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H16O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 244.286 |
| Flash Point | 167.6±22.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 244.109940 |
| PSA | 39.44000 |
| LogP | 3.87 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.557 |
| Storage condition | room temp |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi,Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | GN7700000 |
| HS Code | 29081000 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
| HS Code | 2932209090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932209090. other lactones. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |





![3-[2,4-dimethoxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)phenyl]prop-2-enoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/383/88053-61-6.png)