54952-43-1
| Name | Shikalkin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
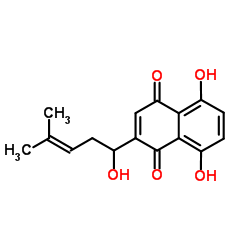
5,8-Dihydroxy-2-(1-hydroxy-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-1,4-naphthoquinone
1,4-Naphthalenedione, 5,8-dihydroxy-2-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-penten-1-yl]- Arnebin-4 1,4-Naphthoquinone, 5,8-dihydroxy-2-(1-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-pentenyl) Alkannin 5,8-Dihydroxy-2-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-penten-1-yl]-1,4-naphthoquinone (±)-Alkannin 5,8-Dihydroxy-2-(1-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-penten-1-yl)-1,4-naphthoquinone (+)-Alkannin 5,8-dihydroxy-2-(1-hydroxy-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)naphthalene-1,4-dione 5,8-Dihydroxy-2-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl]-1,4-naphthoquinone 1,4-Naphthalenedione, 5,8-dihydroxy-2-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-pentenyl]- 1,4-Naphthalenedione, 5,8-dihydroxy-2-(1-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-penten-1-yl)- Shikonin 5,8-Dihydroxy-2-(1-hydroxy-4-methylpent-3-enyl)naphthalene-1,4-dione |
| Description | (Rac)-Shikonin (Shikonin) possesses anti-tumor activity. (Rac)-Shikonin (Shikonin) circumvents cancer drug resistance by induction of a necroptotic death[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Shikonin shows a similar potency toward drug-sensitive cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and HEK293) and their drug-resistant lines overexpressing P-glycoprotein, Bcl-2, or Bcl-xL, which account for most of the clinical cancer drug resistance[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 567.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 149 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C16H16O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 288.295 |
| Flash Point | 311.0±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 288.099762 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| LogP | 4.35 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.642 |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H400 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |