17560-51-9
| Name | metolazone |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MFCD00069304
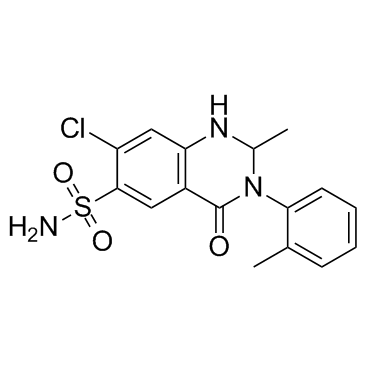
7-chloro-2-méthyl-3-(2-méthylphényl)-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tétrahydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide 7-Chloro-2-methyl-4-oxo-3-(o-tolyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide Xuret 7-Chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-6-quinazolinesulfonamide 7-Chlor-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrochinazolin-6-sulfonamid 7-chloro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide 7-Chloro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinazolinesulfonamide 6-Quinazolinesulfonamide, 7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo- Metolazone 7-chloro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide mykrox tablets EINECS 241-539-3 |
| Description | Metolazone(Zaroxolyn) is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure.Target: OthersMetolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic marketed under the brand names Zytanix from Zydus Cadila, Zaroxolyn, and Mykrox. It is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure. Metolazone indirectly decreases the amount of water reabsorbed into the bloodstream by the kidney, so that blood volume decreases and urine volume increases. This lowers blood pressure and prevents excess fluid accumulation in heart failure. Metolazone is sometimes used together with loop diuretics such as furosemide or bumetanide, but these highly effective combinations can lead to dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities.Metolazone and the other thiazide diuretics inhibit the function of the sodium-chloride symporter, preventing sodium and chloride, and therefore water too, from leaving the lumen to enter the tubule cell. As a result, water remains in the lumen and is excreted as urine, instead of being reabsorbed into the bloodstream. Since most of the sodium in the lumen has already been reabsorbed by the time the filtrate reaches the distal convoluted tubule, thiazide diuretics have limited effects on water balance and on electrolyte levels. Nevertheless, they can be associated with low sodium levels, volume depletion, and low blood pressure, among other adverse effects. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[1]. Stern A. Metolazone, a diuretic agent. Am Heart J. 1976 Feb;91(2):262-3. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 613.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 252-254°C |
| Molecular Formula | C16H16ClN3O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 365.835 |
| Flash Point | 324.9±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 365.060089 |
| PSA | 100.88000 |
| LogP | 1.57 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.629 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | VA1700000 |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2935009090 other sulphonamides VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:35.0% |