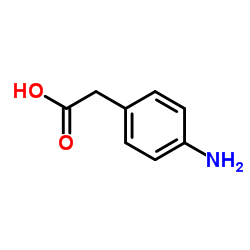
96760-69-9
| Name | [3h]-adac |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Adenosine amine congener hydrate
Adenosine Amine Congener |
| Description | Adenosine amine congener (ADAC) is a selective A1 adenosine receptor agonist, can ameliorate noise- and Cisplatin-induced cochlear injury. Adenosine amine congener also has neuroprotective effects[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
A1 adenosine receptor[1][2] |
| In Vitro | Adenosine amine congener can reduce oxidative stress in the noise-exposed cochlea, leading to protection of sensory hair cells. Adenosine amine congener also can reduce cisplatin-induced apoptosis in cochlear tissues, particularly in sensory hair cells and strial marginal cells. The mechanisms of otoprotection by Adenosine amine congener include inhibition of glutamate release via presynaptic A1 receptors and inhibition of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, which can prevent activation of apoptotic and necrotic cell death pathways[1]. |
| In Vivo | Adenosine amine congener (25-300 μg/kg/day; intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 5 days; male Wistar rats) treatment is most effective in the first 24 hours after noise exposure at doses >50 μg/kg, providing up to 21 dB protection. Adenosine amine congener mitigates noise-induced hearing loss in a dose- and time-dependent manner[1]. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats (8-10 weeks old) treated with noise exposure[1] Dosage: 25 μg/kg/day, 50 μg/kg/day, 100 μg/kg/day, 200 μg/kg/day, and 300 μg/kg/day Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 5 days Result: Most effective in the first 24 hours after noise exposure at doses >50 μg/kg, and provided up to 21 dB protection (averaged across 8-28 kHz). |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C28H32N8O6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 576.60400 |
| Exact Mass | 576.24400 |
| PSA | 209.77000 |
| LogP | 1.21720 |
|
~% 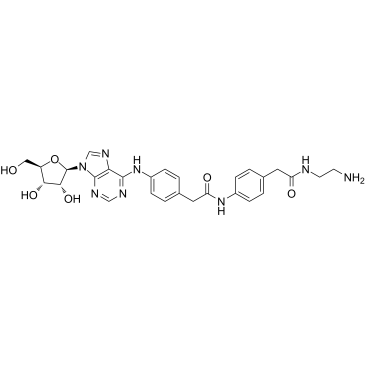
96760-69-9 |
| Literature: Jacobson; Kirk; Padgett; Daly Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1985 , vol. 28, # 9 p. 1341 - 1346 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |