72093-21-1
| Name | mastoparan |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ILE-ASN-LEU-LYS-ALA-LEU-ALA-ALA-LEU-ALA-LYS-LYS-ILE-LEU-NH2
INLKALAALAKKIL INLKALAALAKKIL-NH2 Mastoparan MASTOPARAN VESPULA LEWISII PE PTIDE FROM WASP VEN MFCD00076865 H-ILE-ASN-LEU-LYS-ALA-LEU-ALA-ALA-LEU-ALA-LYS-LYS-ILE-LEU-NH2 MASTOPARAN 4ACOH 6H2O |
| Description | Mastoparan, a tetradecapeptide which is a component of wasp venom, stimulates release of prolactin from cultured rat anterior pituitary cells. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Mastoparan has an amphiphilic nature and is reported to exert a variety of pharmacological and biochemical effects. Mastoparan induces exocytosis of hormones from anterior pituitary cells. Mastoparan stimulation of prolactin secretion is dose-dependent, time-dependent, reversible and required the presence of calcium. Mastoparan causes translocation of protein kinase C activity from a soluble to a membrane-attached form. Mastoparan is able to increase the intracellular Ca2+ concentration in Fura-2-loaded individual lactotrophs. Mastoparan is also able to interact with GTP-bindmg proteins. Thus, Mastoparan has been shown to facilitate exchange of nucleotides and to stimulate GTPase activity on G-proteins. It has therefore been proposed that the cellular effects of Mastoparan are due to an ability to mimic G-protein-linked agonist-liganded receptors[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.15g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1676.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C70H131N19O15 |
| Molecular Weight | 1478.91000 |
| Flash Point | 967.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 1478.01000 |
| PSA | 568.56000 |
| LogP | 7.00350 |
| Appearance | white |
| Index of Refraction | 1.525 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 1 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~75% 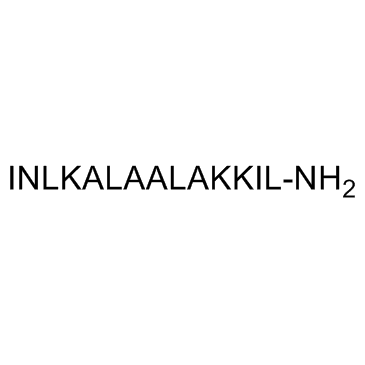
72093-21-1 |
| Literature: Saito, Kazuki; Higashijima, Tsutomu; Miyazawa, Tatsuo; Wakimasu, Mitsuhiro; Fujino, Masahiko Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1984 , vol. 32, # 6 p. 2187 - 2193 |

