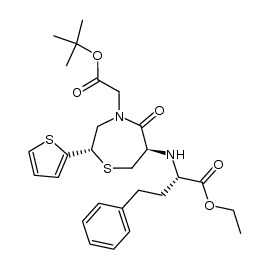
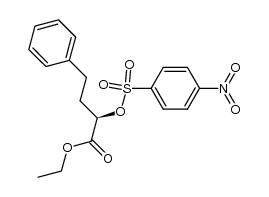
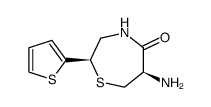
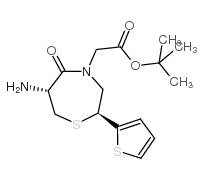
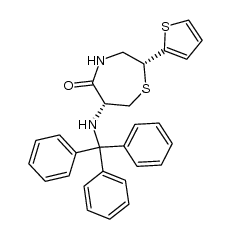
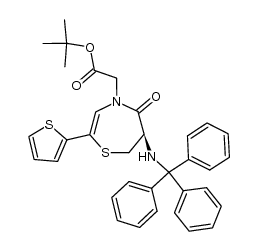
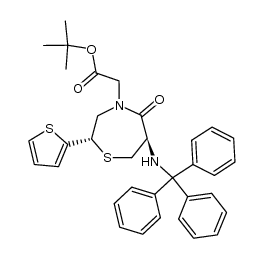
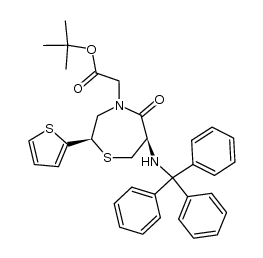
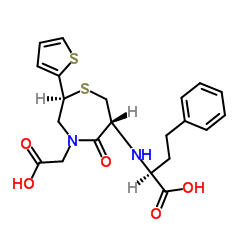
111902-57-9
| Name | 2-[(2S)-6-[[(1S)-1-Ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenyl-propyl]amino]-5-oxo-2-thiophen-2-yl-1,4-thiazepan-4-yl]acetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-[(2S)-6-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenyl-butan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxo-2-thiophen-2-yl-1,4-thiazepan-4-yl]ethanoic acid
2-[(2S)-6-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxo-2-thiophen-2-yl-1,4-thiazepan-4-yl]acetic acid TemocaprilnDiscontinued 2-[(2S)-6-[[(1S)-1-carbethoxy-3-phenyl-propyl]amino]-5-keto-2-(2-thienyl)-1,4-thiazepan-4-yl]acetic acid TEMOCAPRIL 2-((2S,6R)-6-((S)-1-Ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino)-5-oxo-2-(thiophen-2-yl)-1,4-thiazepan-4-yl)aceticacid Temocapil |
| Description | Temocapril is an orally active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Temocapril can be used for the research of hypertension, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, insulin resistance, and renal diseases[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)[1] |
| In Vitro | Temocapril hydrochloride is a prodrug of the ACE inhibitor, Temocaprilat. Temocapril hydrochloride can be readily uptaken via the small intestine, and then be converted to its active metabolite (temocaprilat) by CES1 (human carboxylesterase 1) in the liver[1]. Temocapril hydrochloride (500 nM) reduces the inhibitory effects of RS (N-acetyltetradecapeptide renin substrate) and AngI (angiotensin) on neurogenic vasodilation in the spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR)[2]. Temocapril hydrochloride (0.1-10 μM; 24 h) shows inductive effects on redox proteins thioredoxin (TRX) while no effect on antioxidant enzymes Cu/ZnSOD and Mn-SOD expressions[3]. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: Cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes Concentration: 0.1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Enhanced redox proteins thioredoxin (TRX) expression 1.9-fold at 10 μM without affecting TRX2, Cu/Zn-SOD or Mn-SOD protein expression. |
| In Vivo | Temocapril (10 mg/kg; p.o.; 21 d) enhances cardiomyocyte thioredoxin expression and ameliorates autoimmune myocarditis[3]. Temocapril (30 mg/kg; p.o.; daily; for 4 weeks) suppresses Angiotensin I-induced hypertension, plasma and renal ACE activity, but fails to reduce the level of Ang II in the kidney[4]. Animal Model: Experimental autoimmune myocarditis (EAM) rat model[3] Dosage: 10 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage; administration by water; 21 days Result: Ameliorated EAM and prevented cellular proteins from oxidation. Enhanced cardiomyocyte redox regulatory protein TRX expression. Animal Model: Male Sprague Dawley rats[4] Dosage: 30 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage, daily, for 4 weeks Result: Suppressed the blood pressure elevation induced by Ang I. |
| References |
| Density | 1.33 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 717.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >230ºC (dec) |
| Molecular Formula | C23H28N2O5S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 476.60900 |
| Flash Point | 387.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 476.14400 |
| PSA | 149.48000 |
| LogP | 3.30070 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
|
~78% 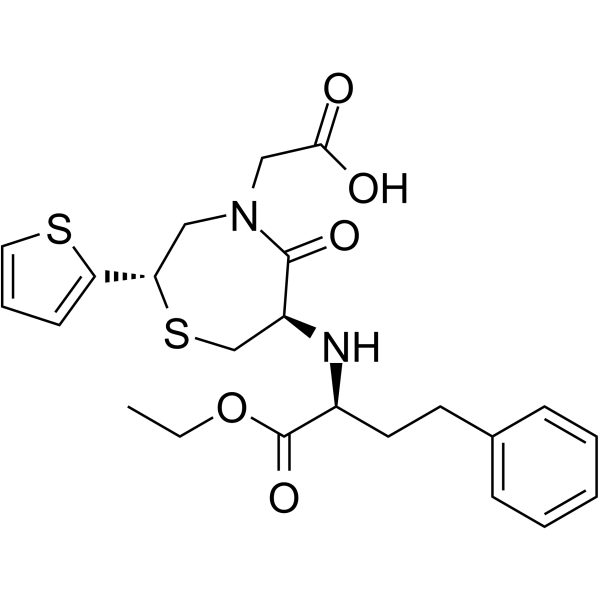
111902-57-9 |
| Literature: Yanagisawa, Hiroaki; Ishihara, Sadao; Ando, Akiko; Kanazaki, Takuro Chemistry Letters, 1989 , p. 137 - 140 |
|
~% 
111902-57-9 |
| Literature: Chemistry Letters, , p. 137 - 140 |
|
~% 
111902-57-9 |
| Literature: Chemistry Letters, , p. 137 - 140 |
|
~% 
111902-57-9 |
| Literature: Chemistry Letters, , p. 137 - 140 |
|
~% 
111902-57-9 |
| Literature: Chemistry Letters, , p. 137 - 140 |
|
~% 
111902-57-9 |
| Literature: Chemistry Letters, , p. 137 - 140 |
|
~% 
111902-57-9 |
| Literature: Chemistry Letters, , p. 137 - 140 |
|
~% 
111902-57-9 |
| Literature: Chemistry Letters, , p. 137 - 140 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |