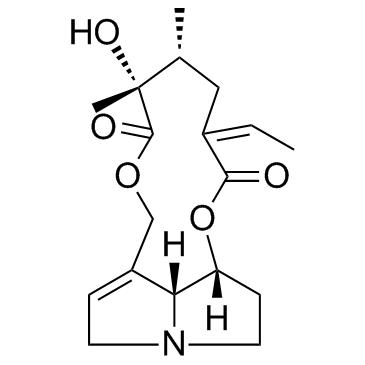
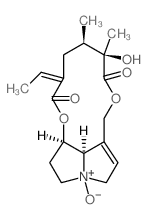
130-01-8
| Name | senecionine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(3Z,5R,6R,14aR,14bR)-3-éthylidène-6-hydroxy-5,6-diméthyl-3,4,5,6,9,11,13,14,14a,14b-décahydro[1,6]dioxacyclododécino[2,3,4-gh]pyrrolizine-2,7-dione
aureine Senecionine MFCD00221720 (3Z,5R,6R,14aR,14bR)-3-Ethyliden-6-hydroxy-5,6-dimethyl-3,4,5,6,9,11,13,14,14a,14b-decahydro[1,6]dioxacyclododecino[2,3,4-gh]pyrrolizin-2,7-dion [1,6]Dioxacyclododecino[2,3,4-gh]pyrrolizine-2,7-dione, 3-ethylidene-3,4,5,6,9,11,13,14,14a,14b-decahydro-6-hydroxy-5,6-dimethyl-, (3Z,5R,6R,14aR,14bR)- (3Z,5R,6R,14aR,14bR)-3-Ethylidene-6-hydroxy-5,6-dimethyl-3,4,5,6,9,11,13,14,14a,14b-decahydro[1,6]dioxacyclododecino[2,3,4-gh]pyrrolizine-2,7-dione (15Z)-12-Hydroxysenecionan-11,16-dione Integerrimine |
| Description | Senecionine is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid isolated from Senecio vulgaris. Senecionine is toxic to animals and humans. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) are considered to be one of the most hepatotoxic groups of compounds of plant origin and are present in about 3% of the world's flowering plants. Most PAs represent a considerable health hazard to both livestock and humans through the consumption of plants and PA-contaminated products such as milk, honey, herbal teas, and medicines[1]. |
| In Vivo | Upon intravenous administration and oral administration of Senecionine and Adonifoline, significant differences in pharmacokinetics were observed, with the Senecionine and Adonifoline being absorbed fast with lower bioavailability and being quickly metabolized to PA N-oxides and hydroxylation products of PAs or their N-oxides[1]. Senecionine fails to stimulate epoxide hydrase, it diminishs the activity of glutathione-s-transferase, aminopyrine demethylase and AHH[2]. Twice-weekly injections of a third constituent, senecionine, beginning on Day 12 or later, results in premature deliveries in three of seven rats, and the pups from all litters are stillborn or die shortly after birth[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[1] Swiss albino rats weighing 155-175 g are incubated for 3 consecutive days with seneciphylline and senecionine at a daily dose of 40 or 80 mg/kg body wt. Control animals received normal saline only. The animals are killed 24 h after the last dose. The livers are removed, weighed and then homogenized in 1.15% KCI, 0.02 HEPES (pH 7.4)[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 563.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 236ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C18H25NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 335.395 |
| Flash Point | 294.7±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 335.173279 |
| PSA | 76.07000 |
| LogP | 0.88 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.570 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Phrases | R25 |
| Safety Phrases | 45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VT5710000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |