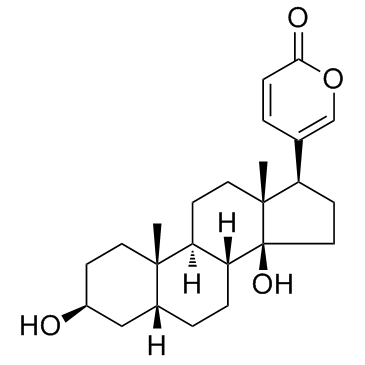
465-21-4
| Name | bufalin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3,14-dihydroxybufa-20,22-dienolide
(3β,5β)-3,14-Dihydroxybufa-20,22-dienolide Bufalin: Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3,14-dihydroxy-, (3b,5b)-, Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3,14-dihydroxy-, (3β,5β)- 5β-Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 3β,14-dihydroxy- 3β,14β-dihydroxy-5β-bufa-20,22-dienolide (3b,5b)-3,14-Dihydroxybufa-20,22-dienolide Bufalin MFCD00056525 |
| Description | Bufalin a major digoxin-like immunoreactive component of the Chinese medicine Chan Su; has been shown to exert a potential for anticancer activity against various human cancer cell lines in vitro.IC50 value:Target: Anticaner natural compoundin vitro: bufalin remarkably inhibited growth in human gallbladder cancer cells by decreasing cell proliferation, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Bufalin also disrupted the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and regulated the expression of cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory molecules. Activation of caspase-9 and the subsequent activation of caspase-3 indicated that bufalin may be inducing mitochondria apoptosis pathways [1]. bufalin suppressed the protein levels associated with DNA damage and repair, such as a DNA dependent serine/threonine protein kinase (DNA-PK), DNA repair proteins breast cancer 1, early onset (BRCA1), 14-3-3 σ (an important checkpoint keeper of DDR), mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1), O6-ethylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) and p53 (tumor suppressor protein) [2]. TNF-α significantly increased p65 translocation into nucleus (P < 0.01) and enhanced NF-κB DNA-binding activity, which were dose-dependently inhibited by bufalin. Furthermore, bufalin attenuated the TNF-α-induced interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), IL-6, and IL-8 production in RAFLSs in a concentration-dependent manner [3]. bufalin enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by activating the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Bufalin also promoted the clustering of death receptor 4 (DR4) and DR5 in aggregated lipid rafts [4].in vivo: bufalin (0.3 and 0.6 mg/kg, i.p.) potently decreased carrageenan-induced paw edema. Bufalin down regulated the expression levels of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) during these treatments [5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 556.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 242 - 243ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C24H34O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 386.524 |
| Flash Point | 189.0±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 386.245697 |
| PSA | 70.67000 |
| LogP | 3.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.594 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300 |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R28 |
| Safety Phrases | 28-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 3462 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | EI2962500 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |