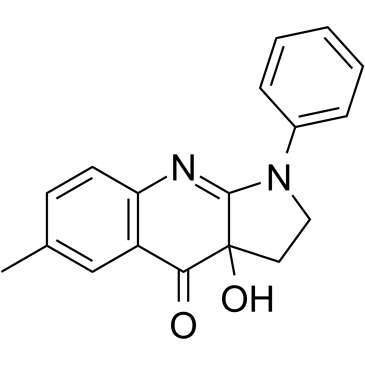
674289-55-5
| Name | blebbistatin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(−)-Blebbistatin
(+/-)-Blebbistatin (3aS)-3a-Hydroxy-6-methyl-1-phenyl-1,2,3,3a-tetrahydro-4H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinolin-4-one Blebbistatin 4H-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinolin-4-one, 1,2,3,3a-tetrahydro-3a-hydroxy-6-methyl-1-phenyl-, (3aS)- (S)-Blebbistatin 3a-hydroxy-6-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-b]quinolin-4-one |
| Description | Blebbistatin is a selective non-muscle myosin II (NMII) inhibitor, promotes directional migration of corneal endothelial cells (CECs) and accelerates wound healing, and better preserves cell junctional integrity and barrier function[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Non-muscle myosin II (NMII)[1] |
| In Vitro | The therapeutic potential of targeting NMII to enhance CEC migration is investigated using bovine corneal endothelial cells (BCECs). Blebbistatin, a direct myosin motor inhibitor, promotes migration and directional persistence in CECs through decreasing actin retrograde flow and increasing lamellipodial protrusion persistence to accelerate wound healing in vitro[1]. |
| In Vivo | Blebbistatin (0.05 mL, 20 μM; intracameral injection; daily; for 6 days; New Zealand white rabbits) treatment promotes wound healing in rabbit corneal endothelial scraping model[1]. Animal Model: New Zealand white rabbits (16-20 weeks; 3-3.5 kg) with injected xylazine 5 mg/kg and ketamine 40 mg/kg[1] Dosage: 0.05 mL; 20 μM Administration: Intracameral injection; daily; for 6 days Result: Resulted in significant improvement of corneal clarity and corneal edema resolution, implying the restoration of an intact corneal endothelial monolayer. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 507.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 210-212ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C18H16N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 292.332 |
| Flash Point | 260.6±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 292.121185 |
| PSA | 52.90000 |
| LogP | 1.62 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.681 |