1268524-70-4
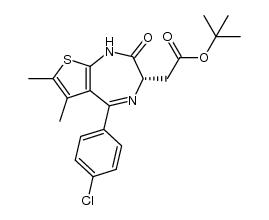
| Name | (S)-tert-butyl 2-(4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3,9-trimethyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]diazepin-6-yl)acetate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(6s)-6-(2-Tert-butoxy-2-oxoethyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3,9-trimethyl-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-F][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-A][1,4]diazepin-10-ium
(+)-JQ1 6H-Thieno[3,2-f][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]diazepine-6-acetic acid, 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3,9-trimethyl-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester, (6S)- JQ1 2-Methyl-2-propanyl [(6S)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3,9-trimethyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]diazepin-6-yl]acetate UNII-1MRH0IMX0W (+)-JQ-1 |
| Description | (+)-JQ-1 is a BET bromodomain inhibitor, with IC50s of 77 and 33 nM for the first and second bromodomain (BRD4(1/2)). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 77/33 nM (BRD4(1/2))[1] |
| In Vitro | (+)-JQ1 represents a potent, highly specific and Kac competitive inhibitor for the BET family of bromodomains. (+)-JQ1 (100 nM, 48 h) prompts squamous differentiation exhibited by cell spindling, flattening and increased expression of keratin. (+)-JQ1 (250 nM) induces rapid expression of keratin in treated NMC 797 cells compared to (-)-JQ1 (250 nM) and vehicle controls, as determined by quantitative immunohistochemistry.(+)-JQ1 (250 nM) elicits a time-dependent induction of strong (3+) keratin staining of treated NMC 797 cells, compared to (-)-JQ1 (250 nM)[1]. (+)-JQ1 is a potent thienodiazepine inhibitor (Kd=90 nM) of the BET family coactivator protein BRD4, which is implicated in the pathogenesis of cancer via transcriptional control of the MYC oncogene. Dose-ranging studies of (+)-JQ1 demonstrates potent inhibition of H4Kac4 binding with a IC50 value of 10 nM for murine BRDT(1) and 11 nM for human BRDT(1)[2]. |
| In Vivo | Matched cohorts of mice with established tumors are randomized to treatment with (+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) or vehicle, administered by daily intraperitoneal injection. Prior to randomization, and after four days of therapy, mice are evaluated by FDG-PET imaging. A marked reduction in FDG uptake is observed with (+)-JQ1 treatment. Tumor-volume measurements confirm a reduction in tumor growth with JQ1 treatment. Pharmacokinetic studies of (+)-JQ1 are performed in CD1 mice following intravenous and oral administration. Mean plasma concentration-time profiles of (+)-JQ1 after intravenous dosing (5 mg/kg). The pharmacokinetic parameters for intravenous (+)-JQ1 demonstrate excellent drug exposure (AUC=2090 hr*ng/mL) and an approximately one hour half-life (T1/2). Mean plasma concentration-time profiles of (+)-JQ1 after oral dosing (10 mg/kg). The pharmacokinetic parameters for oral (+)-JQ1 demonstrate excellent oral bioavailability (F=49%), peak plasma concentration (Cmax=1180 ng/mL) and drug exposure (AUC=2090 hr*ng/mL)[1]. |
| Cell Assay | NUT midline carcinoma patient cell lines (797 and 11060) are plated in T-25 flasks and grown in DMEM (797) or RPMI (11060) containing 10 % fetal bovine serum and 1 % Penicillin/Streptomycin. Cells are treated with either 250 nM (+)-JQ1, 250 nM (-)-JQ1 or the equivalent volume of DMSO (0.025%). At the desired time point, 2×106 cells are spun at 500× g for 5 minutes at 4°C and washed with PBS. Pellets are resuspended in 1 mL of cold PBS and added dropwise while gently vortexing to 9 mL 70 % ethanol in a 15 mL polypropylene centrifuge tube. Fixed cells are then frozen at -20°C overnight. The next day, cells are centrifuged at 500× g for 10 minutes at 4°C and washed with 3 mL of cold PBS. Cells are resuspended in 500 μL of propidium iodide staining solution (0.2 mg/mL RNAse A, 0.02 mg/mL propidium iodide, 0.1 % Triton-X in PBS) and incubated for 20 minutes at 37°C. Samples are then transferred to ice and analyzed on a BD FACS Canto II. Histograms are generated and cell cycle analysis is performed using FlowJo flow cytometry analysis software[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Matched cohorts of mice with established tumors are randomized to treatment with (+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) or vehicle, administered by daily intraperitoneal injection. Male CD1 mice (24-29 g) are treated with a single dose of (+)-JQ1 at 5 mg/kg for intravenous tail vein injection studies and 10 mg/kg for oral gavage studies. Approximately 150 μL of blood are taken from animals by retro-orbital puncture under anesthesia with Isoflurane into EDTA tubes at pre-specified time intervals: 0.033, 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 5, 8 and 24 hours. Three animals are analyzed per time point. Blood samples are put on ice and centrifuged to obtain plasma samples (2000× g, 5 min under 4°C) within 15 minutes post-sampling. Plasma samples are stored at approximately -70°C until analysis is performed. Mice are provided free access to food and water throughout the study. Rats[2] Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats are treated with vehicle or (+)-JQ1 (10 mg/kg). Treatment is administered IP at 1/100 body mass. Rats are checked twice-daily for mortality and weighed on days 1, 3, 7, 14, and 21. The treatment regimen utilized 4 days of 50 mg/kg JQ1 administered daily which is decreased to 10 mg/kg twice daily for the remainder of the study due to the appearance of adverse effects in a subset of animals. For all animals completing 3 weeks of treatment, testis mass, sperm motility, and sperm counts are determined as described for mouse studies. In brief, testes are fixed in Bouin’s and prepared for histology. The other half is minced in warm M16 buffer and used for sperm counts and motility studies. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 610.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C23H25ClN4O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 456.988 |
| Flash Point | 322.9±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 456.138672 |
| PSA | 97.61000 |
| LogP | 4.49 |
| Appearance | white to beige |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.657 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble20mg/mL, clear |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~90% 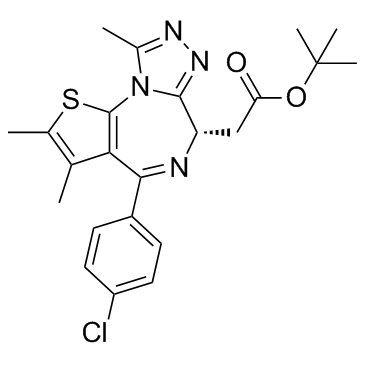
1268524-70-4 |
| Literature: WO2011/143657 A1, ; Page/Page column 82-83 ; |
|
~% 
1268524-70-4 |
| Literature: WO2011/143657 A1, ; |
|
~% 
1268524-70-4 |
| Literature: WO2011/143657 A1, ; |
|
~% 
1268524-70-4 |
| Literature: WO2011/143657 A1, ; |
|
~% 
1268524-70-4 |
| Literature: WO2011/143657 A1, ; |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |