119391-92-3
| Name | n-tert-butyl-d9-phenyl-d5-nitrone |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Phenyl-n-propyl-dimethylsilan
N-[2-(H)Methyl(H)-2-propanyl]-N-[(Z)-(H)phenylmethylene]amine oxide phenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone-d14 Silane,dimethylphenylpropyl Azane, [1,1-di(methyl-d)ethyl-2,2,2-d](phenyl-d-methylene)-, oxide, (Z)- Dimethyl-phenyl-n-propylsilan Phenyl-dimethyl-propyl-silan N-[2-(H)Methyl(H)propan-2-yl]-N-[(Z)-(H)phenylmethylene]amine oxide |
| Description | N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone-d14 is the deuterium labeled N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone[1]. N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone is a nitrone-based free radical scavenger that forms nitroxide spin adducts. N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone inhibits COX2 catalytic activity. N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone has potent ROS scavenging, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-aging and anti-diabetic activities, and can penetrate the blood-brain barrier[2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 283.3±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C11HD14NO |
| Molecular Weight | 191.329 |
| Flash Point | 118.5±15.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 191.203232 |
| PSA | 28.75000 |
| LogP | 1.25 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.552 |
|
~61% 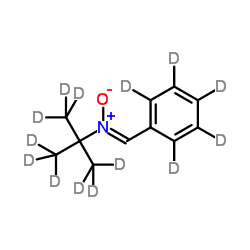
119391-92-3 |
| Literature: Haire, D. Lawrence; Janzen, Edward G. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 1994 , vol. 32, # 3 p. 151 - 157 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |