9007-28-7
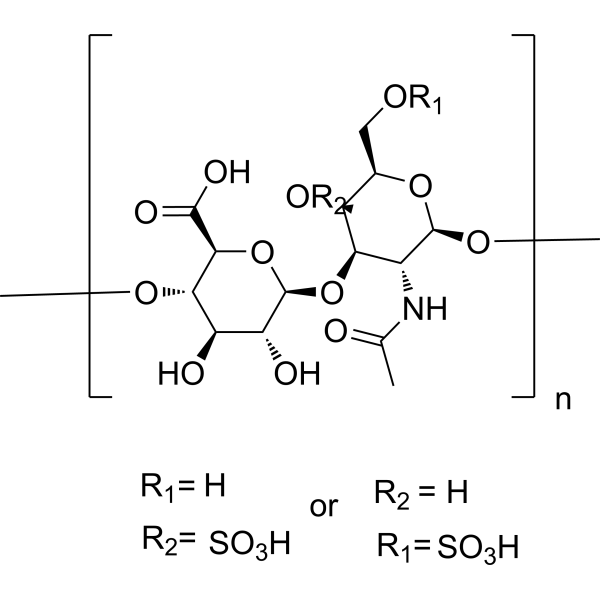
| Name | (5ξ)-2-(Carboxyamino)-2-deoxy-3-O-β-D-glucopyranuronosyl-4-O-sulf o-α-L-arabino-hexopyranose |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cholyltaurine
[14C]-Taurocholic acid α-L-arabino-Hexopyranose, 2-(carboxyamino)-2-deoxy-3-O-β-D-glucopyranuronosyl-, 4-(hydrogen sulfate), (5ξ)- chondroitin-4-sulfate MFCD00146419 EINECS 232-696-9 chonodroitinsufuric acid (5ξ)-2-(Carboxyamino)-2-deoxy-3-O-β-D-glucopyranuronosyl-4-O-sulfo-α-L-arabino-hexopyranose 2-[(R)-4-((3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-hexadecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)pentanoylamino]ethanesulfonic acid Chondroitin (sulfate) |
| Description | Chondroitin sulfate, one of five classes of glycosaminoglycans, has been widely used in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Chondroitin sulfate reduces inflammation mediators and the apoptotic process and is able to reduce protein production of inflammatory cytokines, iNOS and MMPs. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
iNOS[1]MMPs[1] |
| In Vitro | Chondroitin sulfate is a class of sulfated glycosaminoglycans that are linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units composed of uronic acid and N-acetylhexosamine. Several pathogens including parasites, bacteria, and viruses have been shown to utilize cell surface chondroitin sulfate chains to attach to and infect host cells[1]. Chondroitin sulfate occurs naturally in the extracellular matrix of connective tissues, e.g., bone, cartilage, skin, ligaments and tendons. Chondroitin sulfate has been shown to elicit a range of beneficial effects: anti-inflammatory effects, an increase in type II collagen and proteoglycans, a reduction in bone resorption and a better anabolic/catabolic balance in chondrocytes[2]. A large range of chondroitin sulfate concentrations has been used (e.g. 12.5 to 2000 mg/mL, but generally less than200 mg/mL) in in vitro studies. Chondroitin sulfate (200 mg/mL) decreases the chondrocyte susceptibility to single nucleotide polymorphism-induced apoptosis[3]. Chondroitin sulfate reduces inflammation mediators and the apoptotic process and is able to reduce protein production of inflammatory cytokines, iNOS, MMPs[4]. |
| In Vivo | The high content of chondroitin sulfate in the aggrecan plays a major part in allowing cartilage to resist tensile stresses during various loading conditions by providing this tissue with resistance and elasticity. It has been shown that chondroitin sulphate interferes with the progression of structural changes in joint tissues and is used in the management of patients with osteoarthritis[3]. Chondroitin sulfate is mostly administered orally at doses ranging from 800 to 1200mg/day. Chondroitin sulfate is rapidly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. The absorbed chondroitin sulfate reaches the blood compartment as 10% chondroitin sulfate and 90% depolymerized low-molecular-weight derivatives[5]. |
| Cell Assay | Chondrocytes are cultured into six-well culture plates. 12 hours after plating, the culture medium is replaced with 2.0 mL of fresh medium containing LPS at a concentration of 50 mg/mL. 4 hours later, HA, Chondroitin sulfate, HS, keratan sulphate and DS are added separately to each of the wells at concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/mL. The number of viable chondrocytes is then quantified by trypan blue dye exclusion test from several randomly chosen areas of each well[4]. |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | (C14H21NO14S)n |
| Molecular Weight | 479.368 |
| Exact Mass | 479.058105 |
| PSA | 287.45000 |
| LogP | -4.28 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.686 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
|---|