3-Chlorodiphenylamine
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 22:17:54
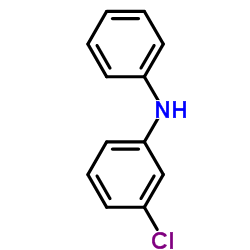
3-Chlorodiphenylamine structure
|
Common Name | 3-Chlorodiphenylamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 101-17-7 | Molecular Weight | 203.667 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 337.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10ClN | Melting Point | 112 °C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 147.4±23.2 °C | |
Use of 3-Chlorodiphenylamine3-Chlorodiphenylamine is a high affinity Ca2+ sensitizer of cardiac muscle. 3-Chlorodiphenylamine is based on diphenylamine and binds to the isolated N-domain of cardiac troponin C (cTnC) (Kd=6 µM). 3-Chlorodiphenylamine is an excellent starting scaffold for the development of more potent Ca2+-sensitizing compounds due to its small size, and can be used for systolic heart failure research[1]. |
| Name | 3-chloro-N-phenylaniline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 3-Chlorodiphenylamine is a high affinity Ca2+ sensitizer of cardiac muscle. 3-Chlorodiphenylamine is based on diphenylamine and binds to the isolated N-domain of cardiac troponin C (cTnC) (Kd=6 µM). 3-Chlorodiphenylamine is an excellent starting scaffold for the development of more potent Ca2+-sensitizing compounds due to its small size, and can be used for systolic heart failure research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Kd: 6 µM (N-domain of cardiac troponin C (cTnC)) Kd: 10 µM (cNTnC–cSp chimera)[1] |
| In Vitro | 3-Chlorodiphenylamine is able to bind highly (Kd=10 µM) to a chimeric protein consisting of the regulatory N-domain of cTnC (cNTnC) and the switch region of cTnI (cNTnC–cSp chimera)[1]. 3-Chlorodiphenylamine (100 µM) results in a 1.5-fold increase in the Ca2+ sensitivity of force development without altering the maximal or resting forces in skinned ventricular trabeculae[1]. 3-Chlorodiphenylamine (25-100 µM) increases Ca2+ sensitivity of the N-domain of intact cTnC after reconstitution into the cTn complex (cTnC complexed with cTnI and cTnT) in a concentration-dependent manner. It exhibits pCa50s with 6.39±0.01, 6.65±0.01, and 6.73±0.02 in the presence of 25, 50, and 100 µM 3-Chlorodiphenylamine, respectively[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 337.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 112 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10ClN |
| Molecular Weight | 203.667 |
| Flash Point | 147.4±23.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 203.050171 |
| PSA | 12.03000 |
| LogP | 3.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.643 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37 |
| HS Code | 2921440000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921440000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921440000. diphenylamine and its derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:17.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
| Benzenamine, 3-chloro-N-phenyl- |
| (3-Chlor-phenyl)-phenyl-amin |
| EINECS 202-922-0 |
| 3-chloro-N-phenyl-aniline |
| 3-Chloro-N-phenyl-benzenamine |
| N-(3-Chlorophenyl)aniline |
| MFCD00000590 |
| N-(m-Chlorophenyl)aniline |
| (3-chlorophenyl)phenylamine |
| (3-Cl-C6H4)PhNH |
| m-Chlorodiphenylamine |
| 3-Chloro-N-phenylaniline |
| 3-Chlorodiphenylamine |
| Benzenamine,3-chloro-N-phenyl |
| N-(3-chlorophenyl)-N-phenylamine |
 CAS#:639-58-7
CAS#:639-58-7 CAS#:108-42-9
CAS#:108-42-9 CAS#:625-99-0
CAS#:625-99-0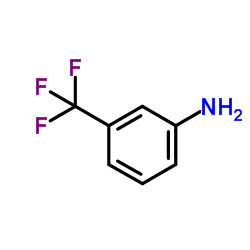 CAS#:98-16-8
CAS#:98-16-8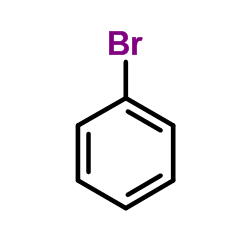 CAS#:108-86-1
CAS#:108-86-1 CAS#:33948-36-6
CAS#:33948-36-6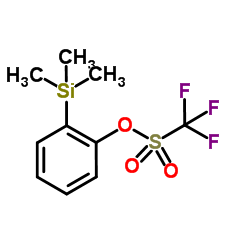 CAS#:88284-48-4
CAS#:88284-48-4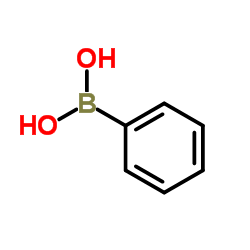 CAS#:98-80-6
CAS#:98-80-6 CAS#:73347-61-2
CAS#:73347-61-2 CAS#:92-39-7
CAS#:92-39-7 CAS#:7369-69-9
CAS#:7369-69-9 CAS#:50-53-3
CAS#:50-53-3 CAS#:2095-17-2
CAS#:2095-17-2 CAS#:16189-69-8
CAS#:16189-69-8 CAS#:106336-13-4
CAS#:106336-13-4 CAS#:10537-08-3
CAS#:10537-08-3 CAS#:6853-90-3
CAS#:6853-90-3 CAS#:95468-02-3
CAS#:95468-02-3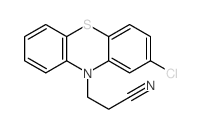 CAS#:4414-83-9
CAS#:4414-83-9
