Keramamine A
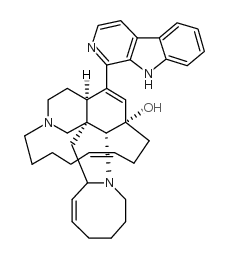
Keramamine A structure
|
Common Name | Keramamine A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104196-68-1 | Molecular Weight | 548.76100 | |
| Density | 1.26g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 756.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C36H44N4O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 411.4ºC | |
Use of Keramamine AManzamine A, an orally active beta-carboline alkaloid, inhibits specifically GSK-3β and CDK-5 with IC50s of 10.2 μM and 1.5 μM, respectively. Manzamine A targets vacuolar ATPases and inhibits Autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Manzamine A has antimalarial and anticancer activities. Manzamine A also shows potent activity against HSV-1[1][2][3][4]. |
| Name | manzamine A |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Manzamine A, an orally active beta-carboline alkaloid, inhibits specifically GSK-3β and CDK-5 with IC50s of 10.2 μM and 1.5 μM, respectively. Manzamine A targets vacuolar ATPases and inhibits Autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Manzamine A has antimalarial and anticancer activities. Manzamine A also shows potent activity against HSV-1[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Plasmodium GSK-3β:10.2 μM (IC50) CDK5:1.5 μM (IC50) vacuolar ATPases Malaria HSV-1 |
| In Vitro | Manzamine A (5-50 µM, 18 h) decreases tau phosphorylation, measured with ELISA[1]. Manzamine A (10 µM) inhibits yeast S. cerevisiae growth by 30%[2]. Manzamine A displays a few enlarged vacuoles in yeast[2]. Manzamine A (2.5-10 µM, 24 h) increases acidity in pancreatic cancer cells and non-malignant Vero cells[2]. Manzamine A (1 µM, 24 h) inhibits HSV-1 infection in SIRC cells[4]. Manzamine A shows antimalarial activity with an IC50 of 8.0 nM (D6 clone) and 11 nM (W2 clone)[5]. Cell Viability Assay[4] Cell Line: SIRC cell Concentration: 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5, and 10 µM Incubation Time: 72 h Result: Inhibited SIRC cell viability with an IC50 of 5.6 µM. |
| In Vivo | Manzamine A (50 and 100 mol/kg, p.o. or i.p.) inhibits the growth of the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei in infected mice[6]. Manzamine A (8 mg/kg, i.p., daily for 8 consecutive days) prolongs the survival of SW mice to 20 days[7]. Animal Model: Plasmodium berghei in infected mice[6] Dosage: 50 or 100 mol/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) or oral administration (p.o.) Result: Inhibited the growth of the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei. Prolonged the survival of highly parasitaemic mice. |
| References |
| Density | 1.26g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 756.6ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C36H44N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 548.76100 |
| Flash Point | 411.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 548.35200 |
| PSA | 55.39000 |
| LogP | 6.73160 |
| Vapour Pressure | 4.65E-24mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.701 |
|
~% 
Keramamine A CAS#:104196-68-1 |
| Literature: Choo, Yeun-Mun; Hamann, Mark T. Heterocycles, 2007 , vol. 71, # 2 p. 245 - 252 |
|
~% 
Keramamine A CAS#:104196-68-1 |
| Literature: Choo, Yeun-Mun; Hamann, Mark T. Heterocycles, 2007 , vol. 71, # 2 p. 245 - 252 |
|
~% 
Keramamine A CAS#:104196-68-1 |
| Literature: Jakubec, Pavol; Hawkins, Alison; Felzmann, Wolfgang; Dixon, Darren J. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012 , vol. 134, # 42 p. 17482 - 17485 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| (4S)-1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid 2-[4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl Methyl Ester |
| (+)-manidipine |
| (S)-Manidipine |
| MANZAMINE A |
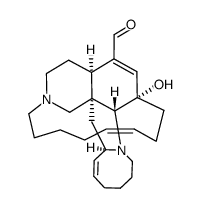
![1-Bromo-9H-pyrido[3,4-b] indole structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/422/159898-15-4.png)