Carbendazim
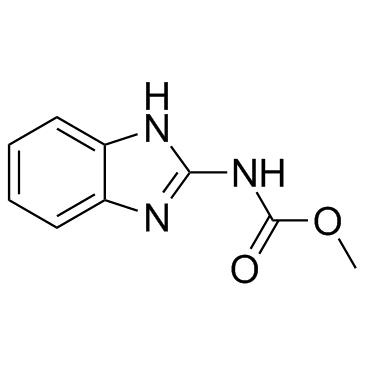
Carbendazim structure
|
Common Name | Carbendazim | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 10605-21-7 | Molecular Weight | 191.187 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 406.1±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H9N3O2 | Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 199.4±24.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of CarbendazimCarbendazim is a broad-spectrum benzimidazole fungicide which can be used to control a broad range of diseases on arable crops, fruits, vegetables, ornamentals and medicinal herbs. |
| Name | carbendazim |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Carbendazim is a broad-spectrum benzimidazole fungicide which can be used to control a broad range of diseases on arable crops, fruits, vegetables, ornamentals and medicinal herbs. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 406.1±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H9N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 191.187 |
| Flash Point | 199.4±24.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 191.069473 |
| PSA | 67.01000 |
| LogP | 2.10 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.650 |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H340-H360FD-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P273-P308 + P313-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R46;R60;R61;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S60-S61-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DD6500000 |
| HS Code | 2933990013 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
The complex contributions of genetics and nutrition to immunity in Drosophila melanogaster.
PLoS Genet. 11(3) , e1005030, (2015) Both malnutrition and undernutrition can lead to compromised immune defense in a diversity of animals, and "nutritional immunology" has been suggested as a means of understanding immunity and determin... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predicti... |
| Methyl 1H-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate |
| BCM,Methyl 2-benzimidazolecarbamate,Methyl benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate |
| bmk |
| mecarzole |
| Methanol, 1-(1H-benzimidazol-2-ylimino)-1-methoxy-, (E)- |
| Fenbendazole impurity A |
| carbendazol |
| BCM,Carbendazim,Methyl 2-benzimidazolecarbamate |
| myco |
| Methyl hydrogen 1H-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbonimidate |
| BCM |
| Stein |
| methyl N-1H-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate |
| methyl benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate |
| spin |
| MBCA |
| T56 BM DNJ CMVO1 |
| MFCD00055390 |
| Carbamic acid, N-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl-, methyl ester |
| methyl 1H-1,3-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate |
| EINECS 234-232-0 |
| Carbendazim |

