Sucrose octaacetate
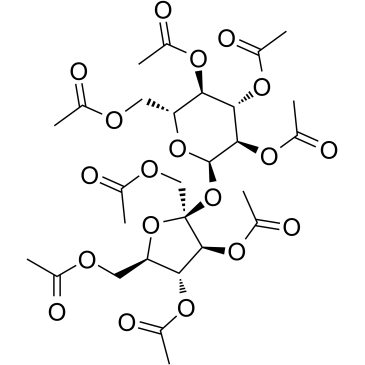
Sucrose octaacetate structure
|
Common Name | Sucrose octaacetate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 126-14-7 | Molecular Weight | 678.590 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 668.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H38O19 | Melting Point | 82-85 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 275.0±31.5 °C | |
Use of Sucrose octaacetateSucrose octaacetate is an acetylated derivative of sucrose with an intensely bitter tasting and can be used as bitter tasting surrogate. Sucrose octaacetate can be used as food additive and also used as an adhesive and plasticizer. Sucrose octaacetate also used in many pesticides, insecticides, and other toxic products as a deterrent to accidental poisoning. Sucrose octaacetate can also be used as an in situ seed and a soft template to synthesize polyaniline (PANI) nanofibers[1][2][3]. |
| Name | Sucrose octaacetate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sucrose octaacetate is an acetylated derivative of sucrose with an intensely bitter tasting and can be used as bitter tasting surrogate. Sucrose octaacetate can be used as food additive and also used as an adhesive and plasticizer. Sucrose octaacetate also used in many pesticides, insecticides, and other toxic products as a deterrent to accidental poisoning. Sucrose octaacetate can also be used as an in situ seed and a soft template to synthesize polyaniline (PANI) nanofibers[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Sucrose octaacetate is nontoxic and has a number of uses based on its bitter taste. For example, sugar is rendered too bitter is eat at a concentration of 0.06% (w/w) Sucrose octaacetate. Sucrose octaacetate can form 255 different possible isomers and degradation products, all of which have a very low molar absorptivity[1]. Polyaniline (PANI) nanofibers and nanorods are obtained using 2 and 3 g Sucrose octaacetate, respectively. The nanostructures containing irregular-shaped agglomerates, such as particulate particles and scaffolds are observed with increasing the concentrations of Sucrose octaacetate. The presence of Sucrose octaacetate during polymerization could only induce a change in morphology, but could not influence the molecular structure of the resulting PANI. Compared with those derived with 1, 3, and 4 g Sucrose octaacetate, the polymerized PANI from 2 g Sucrose octaacetate possesses higher thermal stability and electrical conductivity due to its higher crystallinity and highly ordered structure[3]. |
| In Vivo | No recombination has been found between Sucrose octaacetate-avoidance phenotype and PRP haplotype in any mouse population. Soa and Prp, therefore, are either very near each other or identical. To assess the latter possibility, two type-A, proline-rich protein genes (MP2 and M14), situated approximately 30 kb apart at the Prp locus, are separately transferred from a Sucrose octaacetate-taster inbred strain (SWR) to a Sucrose octaacetate-nontaster inbred strain (FVB). Five MP2-transgenic mice and seven M14-transgenic mice are insensitive to 1 mM Sucrose octaacetate in two-bottle tests, thus retaining the nontaster FVB phenotype. Expression of mRNAs for both type-A Prp genes alone or together do not enhance SOA taste sensitivity in nontaster mice[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 668.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 82-85 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C28H38O19 |
| Molecular Weight | 678.590 |
| Flash Point | 275.0±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 678.200745 |
| PSA | 238.09000 |
| LogP | 3.19 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.509 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | SLIGHTLY SOLUBLE |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| HS Code | 2940000000 |
|---|
|
Stimulation of the extracellular Ca²⁺-sensing receptor by denatonium.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 416(3-4) , 433-6, (2011) The extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor (CASR) is a promiscuous G-protein-coupled receptor closely related to the taste receptors T1R1-T1R3. Here we analyzed the possibility that apart from being st... |
|
|
Gustatory responsiveness to six bitter tastants in three species of nonhuman primates.
J. Chem. Ecol. 35(5) , 560-71, (2009) Gustatory responsiveness of six adult squirrel monkeys, four spider monkeys, and five pigtail macaques to six bitter tastants was assessed in two-bottle preference tests of brief duration (2 min). Ani... |
|
|
B6-MSM consomic mouse strains reveal multiple loci for genetic variation in sucrose octaacetate aversion.
Behav. Genet. 41(5) , 716-23, (2011) Based on crosses among inbred strains derived principally from M. m. domesticus, sucrose octaacetate (SOA) aversion in laboratory mice has been thought for many years to be controlled by a single gene... |
| D-SucroseOctoacetate |
| aacetate |
| sucrose octa-acetate |
| Soa |
| 1,3,4,6-Tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-fructofuranosyl 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-α-D-glucopyranoside |
| Octa-O-acetyl D-(+)-Saccharose |
| Sucrose Octaacetate |
| α-D-Glucopyranoside, 1,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-fructofuranosyl, tetraacetate |
| SUCROSE OCTACETATE |
| Sucroseoctaacetate |
| Sucrose OCLaacetate |
| Octa-O-acetyl D-(+)-Sucrose |
| D-(+)-Sucroseoctaacetate |
| octa-O-acetyl-sucrose |
| EINECS 204-772-1 |
| OCTAACETYLSUCROSE |
| Sucrose octa actate |
| D-(+)-Saccharose Octaacetate |
| MFCD00006623 |
| D-(+)-Sucrose Octaacetate |
| 1,3,4,6-Tetra-O-acetyl-b-D-fructofuranosyl 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-a-D-glucopyranoside |
 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7 CAS#:57-50-1
CAS#:57-50-1 CAS#:1092961-95-9
CAS#:1092961-95-9 CAS#:108-22-5
CAS#:108-22-5 CAS#:102069-21-6
CAS#:102069-21-6 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7 CAS#:115520-96-2
CAS#:115520-96-2![[2-[3,4-dioctadecanoyloxy-2,5-bis(octadecanoyloxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-3,5-dioctadecanoyloxy-6-(octadecanoyloxymethyl)oxan-4-yl] octadecanoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/279/34816-22-3.png) CAS#:34816-22-3
CAS#:34816-22-3 CAS#:79-20-9
CAS#:79-20-9![[2-[3,4-dihexadecanoyloxy-2,5-bis(hexadecanoyloxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-3,5-dihexadecanoyloxy-6-(hexadecanoyloxymethyl)oxan-4-yl] hexadecanoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/482/39024-75-4.png) CAS#:39024-75-4
CAS#:39024-75-4
