chitin
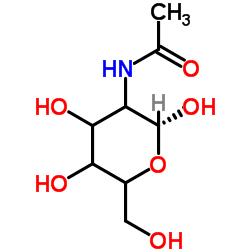
chitin structure
|
Common Name | chitin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1398-61-4 | Molecular Weight | N/A | |
| Density | 1.37 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 522.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | (C8H13NO5)n | Melting Point | >300°C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 269.8ºC | |
Use of chitinChitin, also known as chitin, is a variety of sugars extracted from the shells of marine crustaceans. In nature, chitin widely exists in festival animals such as shrimp, crabs, and worms. |
| Name | chitin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chitin, also known as chitin, is a variety of sugars extracted from the shells of marine crustaceans. In nature, chitin widely exists in festival animals such as shrimp, crabs, and worms. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| Density | 1.37 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 522.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300°C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | (C8H13NO5)n |
| Flash Point | 269.8ºC |
| PSA | 119.25000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.6 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R22:Harmful if swallowed. |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25-36-26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | FM6300000 |
|
In situ continuous growth formation of synthetic biominerals.
Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 49(33) , 3407-9, (2013) Continuous self-assembled growth of both the organic and inorganic components of materials with nacre-like structure is achieved upon mineralisation of chitin and chitosan scaffolds using a combined s... |
|
|
Listeria monocytogenes has a functional chitinolytic system and an active lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase.
FEBS J. 282(5) , 921-36, (2015) Chitinases and chitin-active lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) are most commonly associated with chitin metabolism, but are also reported as virulence factors in pathogenic bacteria. Listeri... |
|
|
Slow Off-rates and Strong Product Binding Are Required for Processivity and Efficient Degradation of Recalcitrant Chitin by Family 18 Chitinases.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 29074-85, (2015) Processive glycoside hydrolases are the key components of enzymatic machineries that decompose recalcitrant polysaccharides, such as chitin and cellulose. The intrinsic processivity (P(Intr)) of cellu... |
| EINECS 215-744-3 |
| CHITOSAN 10 |
| C 7170 |
| Clandosan |
| Poly-(1→4)-β-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine |
| Chitin |
| Hexopyranose, 2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-, (1R)- |
| MFCD00466914 |
| (1R)-2-Acetamido-2-deoxyhexopyranose |
| CHITOSAN 100 |
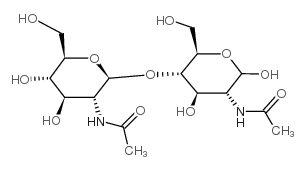 CAS#:35061-50-8
CAS#:35061-50-8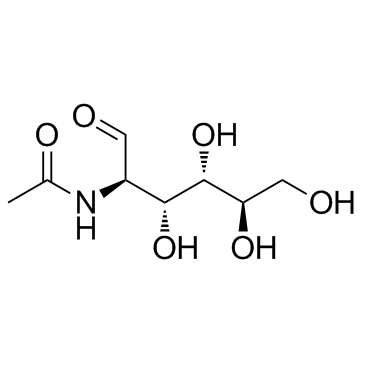 CAS#:7512-17-6
CAS#:7512-17-6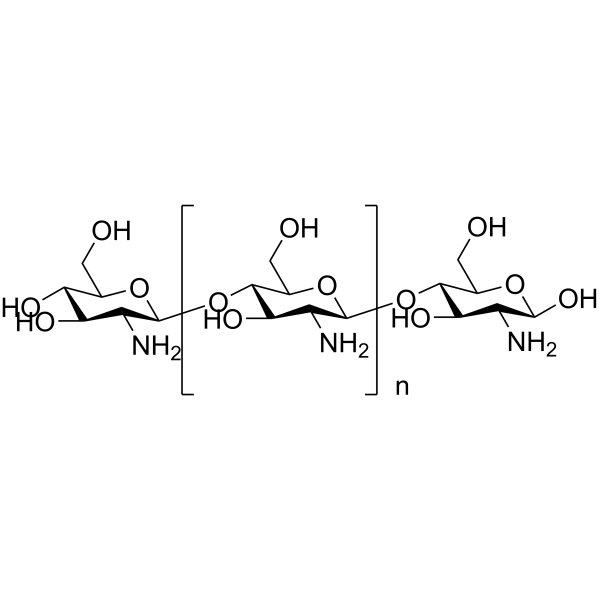 CAS#:9012-76-4
CAS#:9012-76-4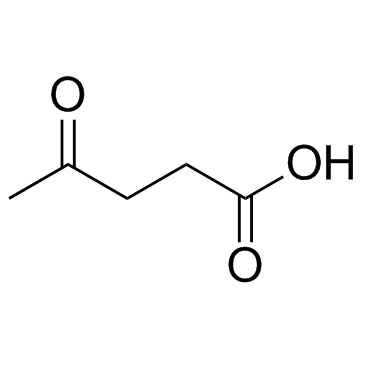 CAS#:123-76-2
CAS#:123-76-2
