Chitosan
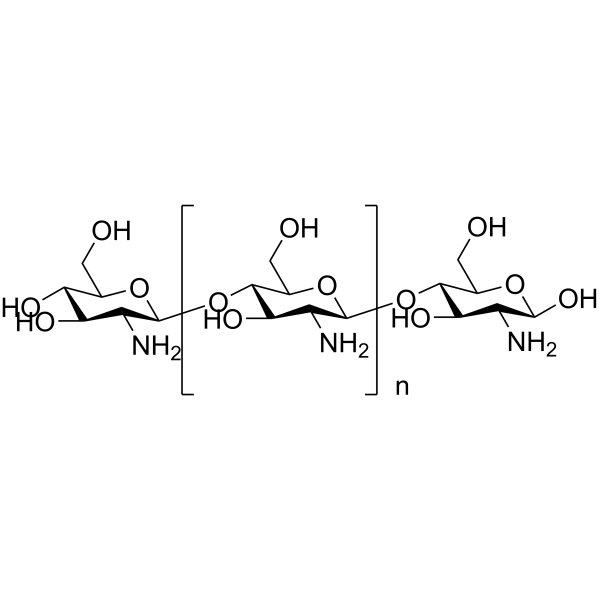
Chitosan structure
|
Common Name | Chitosan | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9012-76-4 | Molecular Weight | 161.16 (monomer) | |
| Density | 1.75g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | (C6H13NO5)n | Melting Point | 88ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of ChitosanChitosan is a natural polycationic linear polysaccharide derived from chitin. |
| Name | chitosan |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chitosan is a natural polycationic linear polysaccharide derived from chitin. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Chitosans are recognized as versatile biomaterials because of their non-toxicity, low allergenicity, biocompatibility and biodegradability. Chitosan is reported to have other biological properties, such as antitumor, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities. It can be used in water treatment, wound-healing materials, pharmaceutical excipient or drug carrier, obesity treatment and as a scaffold for tissue engineering[1]. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan has been demonstrated against many bacteria, filamentous fungi and yeasts. Chitosan has wide spectrum of activity and high killing rate against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, but lower toxicity toward mammalian cells[2]. Chitosan exhibits antitumor activity against different types of cancer. For example, chitosan decreases adhesion of primary melanoma A375 cell line and decreases proliferation of primary melanoma SKMEL28 cell line, it has potent pro-apoptotic effects against RPMI7951, a metastatic melanoma cell line[3]. Chitosan and its derivatives act as antioxidants by scavenging oxygen radicals such as hydroxyl, superoxide, alkyl as well as highly stable DPPH radicals in vitro[4]. |
| In Vivo | Chitosan treatment dramatically increases lifespan and inhibits tumor metastasis especially in treatment groups of the low-molecular weight compound[5]. Chitosan has some apparent treatment effects on rat PCP by reducing HSP70 mRNA expression and lung inflammation, increasing the concentrations of IL-10 and IFN-γ as well as CD4(+) T-lymphocyte numbers, reducing the CD8(+) T-lymphocyte numbers and the concentration of TNF-α and inducing significant ultrastructural damage to P. carinii[6]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.75g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 88ºC |
| Molecular Formula | (C6H13NO5)n |
| Molecular Weight | 161.16 (monomer) |
| Index of Refraction | 1.7 |
| Storage condition | room temp |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | dilute aqueous acid (pH <6.5).: soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22-36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | - |
| RTECS | FM6300000 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|
~% 
Chitosan CAS#:9012-76-4 |
| Literature: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, , vol. 48, # 6 p. 2625 - 2627 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Chitosan oligosaccharides prevented retinal ischemia and reperfusion injury via reduced oxidative stress and inflammation in rats.
Exp. Eye Res. 130 , 38-50, (2015) The purpose of the present study was to investigate the protective effect and mechanism of chitosan oligonucleotides (COS) on retinal ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury. Rats pretreated with PBS, l... |
|
|
Cell–scaffold interaction within engineered tissue
Exp. Cell Res. 323(2) , 346-51, (2014) The structure of a tissue engineering scaffold plays an important role in modulating tissue growth. A novel gelatin–chitosan (Gel–Cs) scaffold with a unique structure produced by three-dimensional pri... |
|
|
Structural insights into the substrate-binding mechanism for a novel chitosanase.
Biochem. J. 461(2) , 335-45, (2014) Chitosanase is able to specifically cleave β-1,4-glycosidic bond linkages in chitosan to produce a chito-oligomer product, which has found a variety of applications in many areas, including functional... |
| EINECS 222-311-2 |
| Poly(beta-(1,4)-D-glucosamine) |
| Poly(beta-(1,4)-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose) |
| MFCD00161512 |
| Chitosan |
 CAS#:66-84-2
CAS#:66-84-2
