Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside
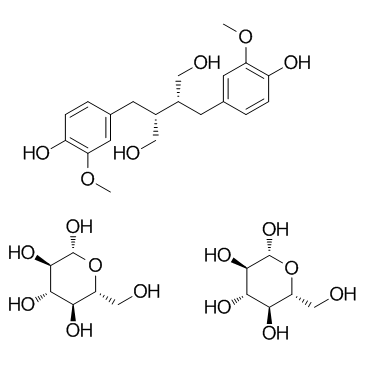
Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside structure
|
Common Name | Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 148244-82-0 | Molecular Weight | 722.73 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 989.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C32H50O18 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 552.0±34.3 °C | |
Use of Secoisolariciresinol Diglucosideseco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside, a synthetic lignin, which is derived from the natural plant flaxseed. seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside reduces asbestos-induced NLRP3 expression, and NF-κB activation in macrophages (MF). seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside also activates Nrf2. |
| Name | Seco-isolariciresinol diglucoside |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside, a synthetic lignin, which is derived from the natural plant flaxseed. seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside reduces asbestos-induced NLRP3 expression, and NF-κB activation in macrophages (MF). seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside also activates Nrf2. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NLRP3 NF-κB Nrf2 |
| In Vitro | seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside (LGM2605) is a nontoxic lignan with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties and is evaluated for protection from asbestos in murine peritoneal macrophages (MF). seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside significantly reduces NLRP3 ranging from 40 to 81%, IL-1β by 89-96%, and TNFα by 67-78%, as well as activated NF-κB by 48-49% while decreasing levels of nitrates/nitrites by 85-93%. seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside reduces asbestos-induced NLRP3 expression, proinflammatory cytokine release, NF-κB activation, and nitrosative stress in macrophages (MF) supporting its possible use in preventing the asbestos-induced inflammatory cascade leading to malignancy. seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside inhibits NF-κB expression and prevents asbestos-induced iNOS expression and nitric oxide production by murine peritoneal macrophages. seco-Isolariciresinol Diglucoside activates Nrf2 and induces the expression of cellular antioxidant and detoxification enzymes[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 989.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C32H50O18 |
| Molecular Weight | 722.73 |
| Flash Point | 552.0±34.3 °C |
| PSA | 257.68000 |
| LogP | -2.79 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.655 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Further studies on a human intestinal bacterium Ruminococcus sp. END-1 for transformation of plant lignans to mammalian lignans.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(16) , 7537-42, (2009) A human intestinal bacterium Ruminococcus (R.) sp. END-1 capable of oxidizing (-)-enterodiol to (-)-enterolactone, enantioselectively, was further investigated from the perspective of transformation o... |
|
|
Production of secoisolariciresinol from defatted flaxseed by bacterial biotransformation.
J. Appl. Microbiol. 113(6) , 1352-61, (2012) Secoisolariciresinol (SECO) is increasingly recognized for potential clinical application because of its preventive effects against breast and colon cancers, atherosclerosis and diabetes, and its prod... |
|
|
Among plant lignans, pinoresinol has the strongest antiinflammatory properties in human intestinal Caco-2 cells.
J. Nutr. 142 , 1798-1805, (2012) Dietary lignans show some promising health benefits, but little is known about their fate and activities in the small intestine. The purpose of this study was thus to investigate whether plant lignans... |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, (2R,3R)-4-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-2,3-bis[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]butyl |
| (2R,3R)-4-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-2,3-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)butyl β-D-glucopyranoside |
| SecoisolariciresinolDiglucoside |
| Flaxseed Extract |
| Secoisolariciresinol Diglucosi |
| Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside |

