Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 10:28:40
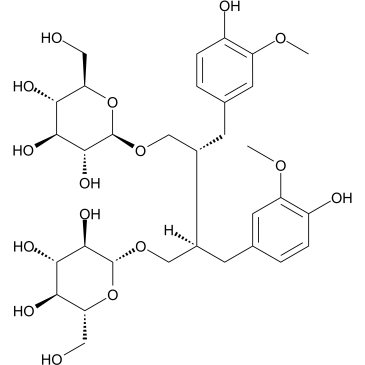
Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside structure
|
Common Name | Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 158932-33-3 | Molecular Weight | 686.698 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 989.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C32H46O16 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 552.0±34.3 °C | |
Use of Secoisolariciresinol diglucosideSecoisolariciresinol diglucoside is a plant lignan isolated from flaxseed, an antagonist of platelet activating factor-receptor, and used as an antioxidant. |
| Name | (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[(2R,3R)-2,3-bis[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-4-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxybutoxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside is a plant lignan isolated from flaxseed, an antagonist of platelet activating factor-receptor, and used as an antioxidant. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Platelet activating factor receptor[1] |
| In Vitro | Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG) inhibition of radiation induces DNA damage in irradiated lung cells. SDG (50 μM) significantly inhibits comet tail length in all cell types. Pre-treatment of SDG equally protects all three types of lung cells from radiation-induced DNA strand breaks. SDG (10-50 µM) alone does not elicit any adverse effect on the colony forming ability of all the three cell types as compared to their respective untreated control cells (100%)[2]. |
| In Vivo | Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG, 15 mg/kg, p.o.) reduces hypercholesterolemic atherosclerosis of rabbits and this effect is releated to a decrease in serum cholesterol, LDL-C, and lipid peroxidation product and an increase in HDL-C and antioxidant reserve. SDG reduces total cholesterol (TC) and LDL-C by 33% and 35%, respectively, at week 8 but increases HDL-C significantly, by > 140%, as early as week 4. It also decreases TC/LDL-C and LDL-C/HDL-C ratios by -64%. There is an increase in aortic malondialdehyde and chemiluminescence in group 3, and they are lower in group 4 than in group 3. SDG reduces hypercholesterolemic atherosclerosis by 73%[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rabbits: New Zealand White rabbits 6 to 8 weeks old weighing between 1.8 and 2.0 kg, after 1 week of adaptation, are assigned to 4 groups. Those in group 1 are fed rabbit laboratory chow pellets. The other groups receive Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG) or cholesterol or cholesterol plus SDG in addition to rabbit chow. The diet does not contain any antioxidants. SDG (15 mg/kg body wt) is fed orally, wrapped in leafy vegetables (lettuce). Water is given ad libitum. The rabbits are housed in cages under a 12-hour-light/12-hour-dark cycle. The rabbits are anesthetized at the end of 8 weeks, and aortas are removed under pentobarbital sodium anesthesia (40 mg/kg IV) for assessment of atherosclerotic plaques and measurement of tissue MDA and antioxidant reserve. Blood samples (from ear marginal artery) for measurement of serum TG, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, and VLDL-C are collected before (time 0) and after 4 and 8 weeks on the respective experimental diets. No food is supplied for 18 hours before withdrawal of blood samples. Weights of the rabbits are recorded at 0, 4, and 8 weeks. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 989.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C32H46O16 |
| Molecular Weight | 686.698 |
| Flash Point | 552.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 686.278564 |
| PSA | 257.68000 |
| LogP | -2.79 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.655 |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, (2R,3R)-4-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-2,3-bis[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]butyl |
| (2R,3R)-4-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-2,3-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)butyl β-D-glucopyranoside |
| Lignans |
| SDG |
| Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside |
| Y0185 |
| X1171 |