demethoxycurcumin
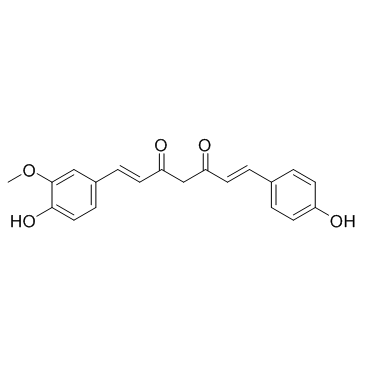
demethoxycurcumin structure
|
Common Name | demethoxycurcumin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22608-11-3 | Molecular Weight | 338.354 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 571.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18O5 | Melting Point | 168ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 205.5±23.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of demethoxycurcuminDemethoxycurcumin(Curcumin II) is a major active curcuminoid; possess anti-inflammatory properties; also exert cytotoxic effects in human cancer cells via induction of apoptosis.IC50 value: Target:in vitro: DMC significantly decreased NO secretion by 35-41% in our inflamed cell model. Decrease in NO production by DMC was concomitant with down-regulation of iNOS at mRNA and protein levels compared to proinflammatory cytokine cocktail and LPS-treated controls. Mechanism of action of DMC may be partly due to its potent inhibition of the iNOS pathway [1]. BDMCCN has the strongest inhibitory activity toward BACE-1 with 17 μM IC50, which was 20 and 13 times lower than those of CCN and DMCCN respectively [2]. Genes associated with DNA damage and repair, cell-cycle check point and apoptosis could be altered by DMC; in particular, 144 genes were found up-regulated and 179 genes down-regulated in NCI-H460 cells after exposure to DMC [3]. in vivo: At low doses, both the curcuminoid mixture and curcumin I did not affect brain stimulation reward, whereas, higher doses increased ICSS thresholds. Curcumin II and curcumin III did not affect brain stimulation reward at any doses. Subthreshold doses of the curcuminoid mixture and curcumin I inhibited the reward-facilitating effect of morphine. |
| Name | demethoxycurcumin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Demethoxycurcumin(Curcumin II) is a major active curcuminoid; possess anti-inflammatory properties; also exert cytotoxic effects in human cancer cells via induction of apoptosis.IC50 value: Target:in vitro: DMC significantly decreased NO secretion by 35-41% in our inflamed cell model. Decrease in NO production by DMC was concomitant with down-regulation of iNOS at mRNA and protein levels compared to proinflammatory cytokine cocktail and LPS-treated controls. Mechanism of action of DMC may be partly due to its potent inhibition of the iNOS pathway [1]. BDMCCN has the strongest inhibitory activity toward BACE-1 with 17 μM IC50, which was 20 and 13 times lower than those of CCN and DMCCN respectively [2]. Genes associated with DNA damage and repair, cell-cycle check point and apoptosis could be altered by DMC; in particular, 144 genes were found up-regulated and 179 genes down-regulated in NCI-H460 cells after exposure to DMC [3]. in vivo: At low doses, both the curcuminoid mixture and curcumin I did not affect brain stimulation reward, whereas, higher doses increased ICSS thresholds. Curcumin II and curcumin III did not affect brain stimulation reward at any doses. Subthreshold doses of the curcuminoid mixture and curcumin I inhibited the reward-facilitating effect of morphine. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 571.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 168ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 338.354 |
| Flash Point | 205.5±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 338.115417 |
| PSA | 83.83000 |
| LogP | 3.15 |
| Appearance of Characters | orange |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.660 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: ≥10mg/mL |
|
~% 
demethoxycurcumin CAS#:22608-11-3 |
| Literature: US2010/48957 A1, ; Page/Page column 4-5 ; |
|
~52% 
demethoxycurcumin CAS#:22608-11-3 |
| Literature: Venkateswarlu, Somepalli; Ramachandra, Marellapudi S.; Subbaraju, Gottumukkala V. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2005 , vol. 13, # 23 p. 6374 - 6380 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Journal of Natural Products, , vol. 61, # 12 p. 1531 - 1534 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Journal of Natural Products, , vol. 61, # 12 p. 1531 - 1534 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Journal of Natural Products, , vol. 61, # 12 p. 1531 - 1534 |
|
~% 
demethoxycurcumin CAS#:22608-11-3 |
| Literature: Molecules, , vol. 16, # 2 p. 1888 - 1900 |
|
~% 
demethoxycurcumin CAS#:22608-11-3 |
| Literature: Molecules, , vol. 16, # 2 p. 1888 - 1900 |
|
Therapeutic potential of turmeric in Alzheimer's disease: curcumin or curcuminoids?
Phytother Res. 28(4) , 517-25, (2014) Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. There is limited choice in modern therapeutics, and drugs available have limited success with multiple side effects in addition to high co... |
|
|
Differential cellular uptake and metabolism of curcuminoids in monocytes/macrophages: regulatory effects on lipid accumulation.
Br. J. Nutr. 112(1) , 8-14, (2014) We have previously shown that curcumin (CUR) may increase lipid accumulation in cultured human acute monocytic leukaemia cell line THP-1 monocytes/macrophages, but that tetrahydrocurcumin (THC), an in... |
|
|
Demethoxycurcumin-induced DNA Damage Decreases DNA Repair-associated Protein Expression Levels in NCI-H460 Human Lung Cancer Cells.
Anticancer Res. 35 , 2691-8, (2015) Demethoxycurcumin (DMC) is a key component of Chinese medicine (Turmeric) and has been proven effective in killing various cancer cells. Its role in inducing cytotoxic effects in many cancer cells has... |
| (1E,6E)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione |
| (1E,6E)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione |
| 1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione, 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)- |
| Demethoxy Curcumin |
| 1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione, 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (1E,6E)- |
| demethoxycurcumin |

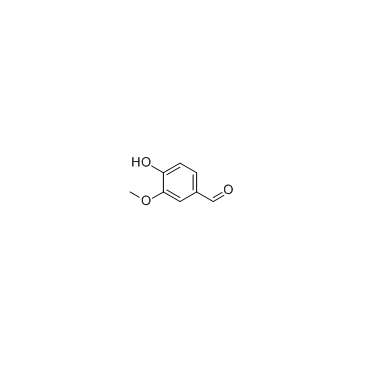
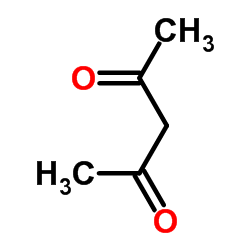
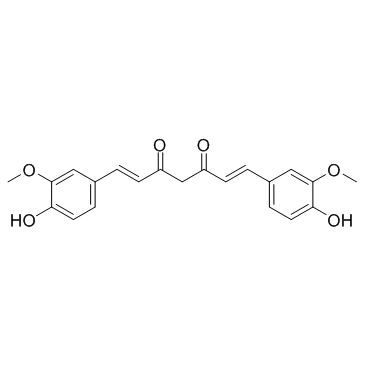
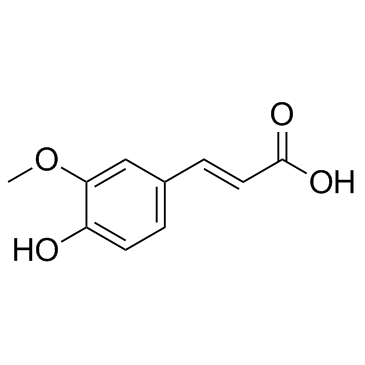 CAS#:1135-24-6
CAS#:1135-24-6 CAS#:7400-08-0
CAS#:7400-08-0
